This is a preprint.
Sde Proteins Coordinate Ubiquitin Utilization and Phosphoribosylation to Promote Establishment and Maintenance of the Legionella Replication Vacuole
- PMID: 37790456
- PMCID: PMC10543313
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3269310/v1
Sde Proteins Coordinate Ubiquitin Utilization and Phosphoribosylation to Promote Establishment and Maintenance of the Legionella Replication Vacuole
Update in
-
Sde proteins coordinate ubiquitin utilization and phosphoribosylation to establish and maintain the Legionella replication vacuole.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 30;15(1):7479. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51272-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39214970 Free PMC article.
Abstract
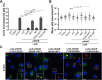
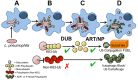
The Legionella pneumophilaSde family of translocated proteins promote host tubular endoplasmic reticulum (ER) rearrangements that are tightly linked to phosphoribosyl-ubiquitin (pR-Ub) modification of Reticulon 4 (Rtn4). Sde proteins have two additional activities of unclear relevance to the infection process: K63 linkage-specific deubiquitination and phosphoribosyl modification of polyubiquitin (pR-Ub). We show here that the deubiquitination activity (DUB) stimulates ER rearrangements while pR-Ub protects the replication vacuole from cytosolic surveillance by autophagy. Loss of DUB activity was tightly linked to lowered pR-Ub modification of Rtn4, consistent with the DUB activity fueling the production of pR-Ub-Rtn4. In parallel, phosphoribosyl modification of polyUb, in a region of the protein known as the isoleucine patch, caused an absolute block in binding by the autophagy adapter p62. An inability of Sde mutants to modify polyUb resulted in immediate p62 association, a critical precursor to autophagic attack. The ability of Sde WT to block p62 association decayed quickly after bacterial infection, as predicted by the presence of previously characterized L. pneumophila effectors that inactivate Sde and remove polyUb. In sum, these results show that the accessory Sde activities act to stimulate ER rearrangements and protect from host innate immune sensing in a temporal fashion.
Keywords: Legionella; autophagy; deubiquitination; intracellular replication; macrophages; ubiquitination.
Figures




References
-
- Cunha B.A., Wu G. & Raza M. Clinical Diagnosis of Legionnaire’s Disease: Six Characteristic Clinical Predictors. Am J Med 128, e21–22 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Cunha B.A., Burillo A. & Bouza E. Legionnaires’ disease. Lancet 387, 376–385 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Safdar N., Crnich C.J. & Maki D.G. The pathogenesis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: its relevance to developing effective strategies for prevention. Respir Care 50, 725–739; discussion 739–741 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

