Effectiveness of Shuxuening injection in coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37790809
- PMCID: PMC10544985
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265603
Effectiveness of Shuxuening injection in coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
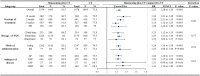
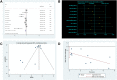
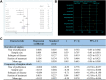
Background: Coronary heart disease (CHD) poses a serious threat to public health, and the current medical management still faces significant challenges. Reliable evidence on the efficacy of Shuxuening injection (SXNI) in CHD is still lacking, even though it is widely used in China. Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of SXNI combination therapy in treating CHD. Methods: A systematic search of eight databases was conducted to identify relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from the inception of each database until June 2023. ROB 2.0, RevMan 5.4, and Stata 15.1 were used for quality evaluation and data analysis. The Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to evaluate the quality of evidence. Results: A total of 3,779 participants from 39 studies were included. The results showed SXNI combination therapy increased the clinical efficacy and decreased the frequency and duration of angina. Furthermore, SXNI combination therapy improved cardiac function of patients by decreasing LVEDD, and increased CI, CO, and LVEF. It also improved blood lipid profiles by increasing HDL, decreasing TC, TG, and LDL. The thrombosis factors of patients were also improved by decreasing FIB, PV, HCT, and HS. Moreover, SXNI combination therapy was superior to the conventional treatment in improving CRP levels, increasing ECG efficacy and BNP. However, due to the limited safety information, reliable safety conclusions could not be drawn. Furthermore, the levels of evidence ranged from very low to moderate due to publication bias and heterogeneity. Conclusion: SXNI can effectively improve angina symptoms, clinical efficacy, cardiac function, blood lipid indicators, and thrombosis factors of patients with CHD. However, more multi-center and large-sample studies are needed to confirm the conclusions due to the limitations of this study. Registration https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=399606; Identifier: CRD42023433292.
Keywords: Shuxuening injection; coronary heart disease; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trial; systematic review.
Copyright © 2023 Shi, Sun, Ji, Ma, Zhao, Yang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cai H. (2021). Efficacy and safety of Shuxuening combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of angina pectoris after acute myocardial infarction. Sichuan J. Physiol. Sci. 43, 302–304.
-
- Chai J. (2010). Shuxuening combined with western medicine in treating 58 cases of unstable angina. FUJIAN J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 41, 20–21. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-338X.2010.03.011 - DOI
-
- Chen B., Chen X., Liang S. (2016). Clinical effect analysis of Shuxuening injection combined with nitroglycerin injection on angina pectoris of coronary heart disease. Chin. Prac. Med. 11, 148–149. 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2016.20.094 - DOI
-
- Cui S., An A., Hao X., Zhao X., Gong J. (2008). Curative effect of shuxuening injection on angina pectoris. Eval. Anal. Drug-Use Hosp. Chin 8, 687–688. 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2124.2008.09.020 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

