Estimated Effectiveness of a Primary Cycle of Protein Recombinant Vaccine NVX-CoV2373 Against COVID-19
- PMID: 37792377
- PMCID: PMC10551773
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36854
Estimated Effectiveness of a Primary Cycle of Protein Recombinant Vaccine NVX-CoV2373 Against COVID-19
Abstract
Importance: Protein recombinant vaccine NVX-CoV2373 (Novavax) against COVID-19 was authorized for its use in adults in late 2021, but evidence on its estimated effectiveness in a general population is lacking.
Objective: To estimate vaccine effectiveness of a primary cycle with NVX-CoV2373 against SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic COVID-19.
Design, setting, and participants: Retrospective cohort study linking data from the national vaccination registry and the COVID-19 surveillance system in Italy during a period of Omicron predominance. All adults starting a primary vaccination with NVX-CoV2373 between February 28 and September 4, 2022, were included, with follow-up ending on September 25, 2022. Data were analyzed in February 2023.
Exposures: Partial (1 dose only) vaccination and full vaccination (2 doses) with NVX-CoV-2373.
Main outcomes and measures: Notified SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic COVID-19. Poisson regression models were used to estimate effectiveness against both outcomes. Adjusted estimated vaccine effectiveness was calculated as (1 - incidence rate ratio) × 100.
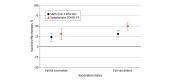
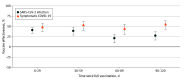
Results: The study included 20 903 individuals who started the primary cycle during the study period. Median (IQR) age of participants was 52 (39-61) years, 10 794 (51.6%) were female, and 20 592 participants (98.5%) had no factors associated with risk for severe COVID-19. Adjusted estimated vaccine effectiveness against notified SARS-CoV-2 infection in those partially vaccinated with NVX-CoV2373 was 23% (95% CI, 13%-33%) and was 31% (95% CI, 22%-39%) in those fully vaccinated. Estimated vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic COVID-19 was 31% (95% CI, 16%-44%) in those partially vaccinated and 50% (95% CI, 40%-58%) in those fully vaccinated. Estimated effectiveness during the first 4 months after completion of the primary cycle decreased against SARS-CoV-2 infection but remained stable against symptomatic COVID-19.
Conclusions and relevance: This cohort study found that, in an Omicron-dominant period, protein recombinant vaccine NVX-CoV2373 was associated with protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptomatic COVID-19. The use of this vaccine could remain an important element in reducing the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Data on COVID-19 vaccination in the EU/EEA. Accessed December 23, 2022. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/data-covid-19-vaccinatio...
-
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità . COVID-19: surveillance, infection impact and vaccine effectiveness. National update 21 September 2022. Article In Italian. 2022. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.epicentro.iss.it/en/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-integrated-survei...
-
- Italian Government. Anti COVID-19 vaccine report. Article in Italian. Accessed December 16, 2022. https://www.governo.it/it/cscovid19/report-vaccini/
-
- Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco . Vaccini COVID-19. Accessed February 20, 2023. https://www.aifa.gov.it/vaccini-covid-19
-
- World Health Organization . Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19 - 14 December 2022. 2022. Accessed September 14, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

