MYL3 protects chondrocytes from senescence by inhibiting clathrin-mediated endocytosis and activating of Notch signaling
- PMID: 37794006
- PMCID: PMC10550997
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41858-7
MYL3 protects chondrocytes from senescence by inhibiting clathrin-mediated endocytosis and activating of Notch signaling
Abstract
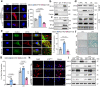
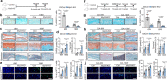
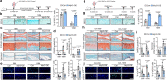
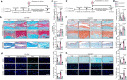
As the unique cell type in articular cartilage, chondrocyte senescence is a crucial cellular event contributing to osteoarthritis development. Here we show that clathrin-mediated endocytosis and activation of Notch signaling promotes chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis development, which is negatively regulated by myosin light chain 3. Myosin light chain 3 (MYL3) protein levels decline sharply in senescent chondrocytes of cartilages from model mice and osteoarthritis (OA) patients. Conditional deletion of Myl3 in chondrocytes significantly promoted, whereas intra-articular injection of adeno-associated virus overexpressing MYL3 delayed, OA progression in male mice. MYL3 deficiency led to enhanced clathrin-mediated endocytosis by promoting the interaction between myosin VI and clathrin, further inducing the internalization of Notch and resulting in activation of Notch signaling in chondrocytes. Pharmacologic blockade of clathrin-mediated endocytosis-Notch signaling prevented MYL3 loss-induced chondrocyte senescence and alleviated OA progression in male mice. Our results establish a previously unknown mechanism essential for cellular senescence and provide a potential therapeutic direction for OA.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Hernandez-Segura A, Nehme J, Demaria M. Hallmarks of cellular senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28:436–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

