Global burden of disease due to rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a mathematical modeling analysis
- PMID: 37794037
- PMCID: PMC10550952
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41937-9
Global burden of disease due to rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a mathematical modeling analysis
Abstract
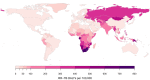
In 2020, almost half a million individuals developed rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis (RR-TB). We estimated the global burden of RR-TB over the lifetime of affected individuals. We synthesized data on incidence, case detection, and treatment outcomes in 192 countries (99.99% of global tuberculosis). Using a mathematical model, we projected disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) over the lifetime for individuals developing tuberculosis in 2020 stratified by country, age, sex, HIV, and rifampicin resistance. Here we show that incident RR-TB in 2020 was responsible for an estimated 6.9 (95% uncertainty interval: 5.5, 8.5) million DALYs, 44% (31, 54) of which accrued among TB survivors. We estimated an average of 17 (14, 21) DALYs per person developing RR-TB, 34% (12, 56) greater than for rifampicin-susceptible tuberculosis. RR-TB burden per 100,000 was highest in former Soviet Union countries and southern African countries. While RR-TB causes substantial short-term morbidity and mortality, nearly half of the overall disease burden of RR-TB accrues among tuberculosis survivors. The substantial long-term health impacts among those surviving RR-TB disease suggest the need for improved post-treatment care and further justify increased health expenditures to prevent RR-TB transmission.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Global TB Report 2022 (WHO, 2022).
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Consolidated Guidelines on Tuberculosis. Module 4: Treatment-drug-resistant Tuberculosis Treatment, 2022 Update (World Health Organization, 2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

