The role of TXNIP in cancer: a fine balance between redox, metabolic, and immunological tumor control
- PMID: 37794178
- PMCID: PMC10703902
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-023-02442-4
The role of TXNIP in cancer: a fine balance between redox, metabolic, and immunological tumor control
Abstract
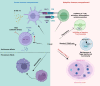
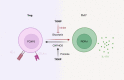
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is commonly considered a master regulator of cellular oxidation, regulating the expression and function of Thioredoxin (Trx). Recent work has identified that TXNIP has a far wider range of additional roles: from regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, to cell cycle arrest and inflammation. Its expression is increased by stressors commonly found in neoplastic cells and the wider tumor microenvironment (TME), and, as such, TXNIP has been extensively studied in cancers. In this review, we evaluate the current literature regarding the regulation and the function of TXNIP, highlighting its emerging role in modulating signaling between different cell types within the TME. We then assess current and future translational opportunities and the associated challenges in this area. An improved understanding of the functions and mechanisms of TXNIP in cancers may enhance its suitability as a therapeutic target.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Nishiyama A, Matsui M, Iwata S, Hirota K, Masutani H, Nakamura H, et al. Identification of thioredoxin-binding protein-2/vitamin D(3) up-regulated protein 1 as a negative regulator of thioredoxin function and expression. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21645–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

