Structural and functional implications of SLC13A3 and SLC9A6 mutations: an in silico approach to understanding intellectual disability
- PMID: 37794328
- PMCID: PMC10548666
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-023-03397-y
Structural and functional implications of SLC13A3 and SLC9A6 mutations: an in silico approach to understanding intellectual disability
Abstract
Background: Intellectual disability (ID) is a condition that varies widely in both its clinical presentation and its genetic underpinnings. It significantly impacts patients' learning capacities and lowers their IQ below 70. The solute carrier (SLC) family is the most abundant class of transmembrane transporters and is responsible for the translocation of various substances across cell membranes, including nutrients, ions, metabolites, and medicines. The SLC13A3 gene encodes a plasma membrane-localized Na+/dicarboxylate cotransporter 3 (NaDC3) primarily expressed in the kidney, astrocytes, and the choroid plexus. In addition to three Na + ions, it brings four to six carbon dicarboxylates into the cytosol. Recently, it was discovered that patients with acute reversible leukoencephalopathy and a-ketoglutarate accumulation (ARLIAK) carry pathogenic mutations in the SLC13A3 gene, and the X-linked neurodevelopmental condition Christianson Syndrome is caused by mutations in the SLC9A6 gene, which encodes the recycling endosomal alkali cation/proton exchanger NHE6, also called sodium-hydrogen exchanger-6. As a result, there are severe impairments in the patient's mental capacity, physical skills, and adaptive behavior.
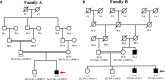
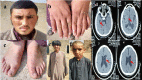
Methods and results: Two Pakistani families (A and B) with autosomal recessive and X-linked intellectual disorders were clinically evaluated, and two novel disease-causing variants in the SLC13A3 gene (NM 022829.5) and the SLC9A6 gene (NM 001042537.2) were identified using whole exome sequencing. Family-A segregated a novel homozygous missense variant (c.1478 C > T; p. Pro493Leu) in the exon-11 of the SLC13A3 gene. At the same time, family-B segregated a novel missense variant (c.1342G > A; p.Gly448Arg) in the exon-10 of the SLC9A6 gene. By integrating computational approaches, our findings provided insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of ID in individuals with SLC13A3 and SLC9A6 mutations.
Conclusion: We have utilized in-silico tools in the current study to examine the deleterious effects of the identified variants, which carry the potential to understand the genotype-phenotype relationships in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Acute reversible leukoencephalopathy; Christianson Syndrome; Exome sequencing; Intellectual disability; Molecular dynamics simulation; SLC13A3; SLC9A6.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A potential gain-of-function variant of SLC9A6 leads to endosomal alkalinization and neuronal atrophy associated with Christianson Syndrome.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Jan;121:187-204. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 30296617
-
Case Report: Compound Heterozygous Variants of SLC13A3 Identified in a Chinese Patient With Acute Reversible Leukoencephalopathy and α-Ketoglutarate Accumulation.Front Pediatr. 2021 Dec 13;9:801719. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.801719. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34966709 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked Christianson syndrome: heterozygous female Slc9a6 knockout mice develop mosaic neuropathological changes and related behavioral abnormalities.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Jan;9(1):13-23. doi: 10.1242/dmm.022780. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 26515654 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding phenotypic spectrum of female SLC9A6 mutation carriers: a case series and review of the literature.Hum Genet. 2016 Aug;135(8):841-50. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1675-5. Epub 2016 May 3. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27142213 Review.
-
A novel PAK3 pathogenic variant identified in two siblings from a Japanese family with X-linked intellectual disability: case report and review of the literature.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2019 Dec 13;5(6):a003988. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a003988. Print 2019 Dec. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2019. PMID: 31444167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SLC9A6-Linked Parkinson Syndrome in Female Heterozygotes Is Associated With PET-Detectable Tau Pathology.Neurol Genet. 2025 Jan 13;11(1):e200235. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200235. eCollection 2025 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2025. PMID: 39810750 Free PMC article.
-
Variants in HCFC1 and MN1 genes causing intellectual disability in two Pakistani families.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jul 2;17(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01943-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38956580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boat TF, Wu J. Committee to evaluate the supplemental security income disability program for children with mental disorders. Board on the Health of Select Populations; 2015.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

