Factors associated with mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa: a multilevel robust Poisson regression modelling
- PMID: 37794438
- PMCID: PMC10552283
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-023-10065-x
Factors associated with mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa: a multilevel robust Poisson regression modelling
Abstract
Background: Timely and appropriate treatment for childhood illness saves the lives of millions of children. In low-middle-income countries such as sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), poor healthcare-seeking behavior for childhood illnesses is identified as a major contributor to the increased risk of child morbidity and mortality. However, studies are limited on Factors associated with mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa.
Objective: To examine factors associated with a mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa.
Methods: A secondary data analysis was conducted based on the latest Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) data of 36 sub-Saharan African countries. A total weighted sample of 16,925 mothers who had under-five children with acute respiratory infection symptoms was considered. The Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC), Median Odds Ratio (MOR), and Likelihood Ratio (LR) tests were done to assess the presence of clustering. Model comparison was made based on deviance (-2LLR) value. Variables with a p-value < 0.2 in the bivariable multilevel robust Poisson analysis were considered for the multivariable analysis. In the multivariable multilevel robust Poisson regression analysis, the Adjusted Prevalence Ratio (APR) with the 95% Confidence Interval (CI) was reported to declare the statistical significance and strength of the association.
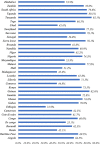
Results: The prevalence of mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children in SSA was 64.9% (95% CI: 64.2%, 65.7%). In the multivariable analysis; mothers who attained primary education (APR = 1.11, 95% CI: 1.08, 1.15), secondary education (APR = 1.13, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.18), and higher education (APR = 1.19, 95% CI: 1.11, 1.27), belonged to the richest household (APR = 1.07: 95% CI: 1.02, 1.12), had media exposure (APR = 1.11, 95% CI: 1.08, 1.15), currently working (APR = 1.08, 95% CI: 1.06, 1.11), had ANC use (APR = 1.25: 95% CI: 1.17, 1.35), health facility delivery (APR = 1.10, 95% CI: 1.07, 1.14), belonged to West Africa (APR = 1.04, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.08) and being in the community with high media exposure (APR = 1.04, 95% CI: 1.02, 1,07) were significantly associated with higher prevalence of mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children. On the other hand, distance to a health facility (APR = 0.87, 95% CI: 0.84, 0.91), and being in central Africa (APR = 0.87, 95% CI: 0.84, 0.91) were significantly associated with a lower prevalence of mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children.
Conclusion: Mother's healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children. It was influenced by maternal education, maternal working status, media exposure, household wealth status, distance to the health facility, and maternal health care service use. Any interventions aiming at improving maternal education, maternal healthcare services, and media access are critical in improving mothers' healthcare-seeking behavior for symptoms of acute respiratory infection in under-five children, hence lowering the prevalence of ARI-related death and morbidity.
Keywords: Mothers healthcare-seeking behavior; Multilevel robust Poisson regression; SSA; Under-five children.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prompt treatment of fever and its associated factors among under-five children in sub-Saharan Africa: A multilevel analysis of evidence from 36 countries.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0303680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303680. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753676 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with the use of antibiotics for children presenting with illnesses with fever and cough obtained from prescription and non-prescription sources: a cross-sectional study of data for 37 sub-Saharan African countries.BMC Public Health. 2024 Apr 19;24(1):1089. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18490-1. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38641808 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with healthcare-seeking behavior for symptomatic acute respiratory infection among children in East Africa: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Nov 15;22(1):662. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03680-w. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36380283 Free PMC article.
-
Acute lower respiratory infections among children under five in Sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review of prevalence and risk factors.BMC Pediatr. 2023 May 6;23(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04033-x. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37149597 Free PMC article.
-
A Scoping Review of the Risk Factors Associated with Anaemia among Children Under Five Years in Sub-Saharan African Countries.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 27;17(23):8829. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17238829. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33261060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influencing factors of patients' behavior of healthcare seeking: a meta-analysis in China.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 28;13:1583075. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1583075. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40356827 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning algorithms to predict healthcare-seeking behaviors of mothers for acute respiratory infections and their determinants among children under five in sub-Saharan Africa.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 19;12:1362392. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1362392. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38962762 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare-Seeking Behaviour for Obstetric Complications in Ethiopia: A Multilevel Mixed-Effect Analysis.Health Serv Insights. 2025 Jun 24;18:11786329251347353. doi: 10.1177/11786329251347353. eCollection 2025. Health Serv Insights. 2025. PMID: 40567355 Free PMC article.
-
Morbidity and health seeking behavior among children and adolescents (0-19 years): a household survey assessment in Northwestern Tanzania.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jul 31;25(1):1011. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-13173-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40745298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams BG, Gouws E, Boschi-Pinto C, Bryce J, Dye C. Estimates of world-wide distribution of child deaths from acute respiratory infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2(1):25–32. - PubMed
-
- Goodarzi E, Sohrabivafa M, Darvishi I, Naemi H, Khazaei Z: Epidemiology of mortality induced by acute respiratory infections in infants and children under the age of 5 years and its relationship with the Human Development Index in Asia: an updated ecological study. J Public Health 2020:1–8.
-
- Feigin VL, Roth GA, Naghavi M, Parmar P, Krishnamurthi R, Chugh S, Mensah GA, Norrving B, Shiue I, Ng M. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(9):913–924. - PubMed
-
- Mokdad AH, Forouzanfar MH, Daoud F, Mokdad AA, El Bcheraoui C, Moradi-Lakeh M, Kyu HH, Barber RM, Wagner J, Cercy K. Global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors for young people's health during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;387(10036):2383–2401. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous