Identification and functional analysis of serine protease inhibitor gene family of Eocanthecona furcellata (Wolff)
- PMID: 37795265
- PMCID: PMC10545863
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1248354
Identification and functional analysis of serine protease inhibitor gene family of Eocanthecona furcellata (Wolff)
Abstract
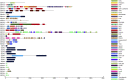
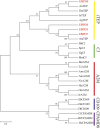
The predatory natural enemy Eocanthecona furcellata plays a crucial role in agricultural ecosystems due to its effective pest control measures and defensive venom. Predator venom contains serine protease inhibitors (SPIs), which are the primary regulators of serine protease activity and play key roles in digestion, development, innate immunity, and other physiological regulatory processes. However, the regulation mechanism of SPIs in the salivary glands of predatory natural enemies is still unknown. In this study, we sequenced the transcriptome of E. furcellata salivary gland and identified 38 SPIs genes named EfSPI1∼EfSPI38. Through gene structure, multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis, real-time quantitative PCR (RT-PCR) expression profiles of different developmental stages and different tissues were analyzed. RNAi technology was used to explore the gene function of EFSPI20. The results showed that these 38 EfSPIs genes contained 8 SPI domains, which were serpin, TIL, Kunitz, Kazal, Antistasin, Pacifastin, WAP and A2M. The expression profile results showed that the expression of different types of EfSPIs genes was different at different developmental stages and different tissues. Most of the EfSPIs genes were highly expressed in the egg stage. The EfSPI20, EfSPI21, EfSPI22, and EfSPI24 genes of the Pacifastin subfamily and the EfSPI35 gene of the A2M subfamily were highly expressed in the nymphal and adult stages, which was consistent with the RT-qPCR verification results. These five genes are positively correlated with each other and have a synergistic effect on E. furcellata, and they were highly expressed in salivary glands. After interfering with the expression of the EfSPI20 gene, the survival rate and predatory amount of male and female adults were significantly decreased. Taken together, we speculated some EfSPIs may inhibit trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase, and some EfSPIs may be involved in autoimmune responses. EfSPI20 was essential for the predation and digestion of E. furcellata, and the functions of other EfSPIs were discussed. Our findings provide valuable insights into the diversity of EfSPIs in E. furcellata and the potential functions of regulating their predation, digestion and innate immunity, which may be of great significance for developing new pest control strategies.
Keywords: Eocanthecona furcellata (Wolff); RNA interference; natural enemy; salivary gland; serine protease inhibitor.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Dai, Chen, Qin, Zhu, Zhu, Chen, Ding, Wu and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors GC and YD were employed by Yunan Tobacco Company Chuxiong Prefecture Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Agusti N., Cohen A. C. (2000). Lygus hesperus and L. lineolares (Hemiptera: miridae), phytophages, zoophages, or omnivores: evidence of feeding adaptations suggested by the salivary and midgut digestive enzymes. J. Entomological Sci. 35, 176–186. 10.18474/0749-8004-35.2.176 - DOI
-
- Beak J. H., Lee S. H. (2014). Differential gene expression profiles in the salivary gland of Orius laevigatus . J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 17, 729–735. 10.1016/j.aspen.2014.06.015 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

