Engineered small extracellular vesicle-mediated NOX4 siRNA delivery for targeted therapy of cardiac hypertrophy
- PMID: 37795828
- PMCID: PMC10552075
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12371
Engineered small extracellular vesicle-mediated NOX4 siRNA delivery for targeted therapy of cardiac hypertrophy
Abstract
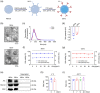
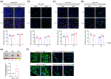
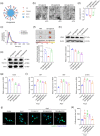
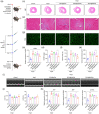
Small-interfering RNA (siRNA) therapy is considered a powerful therapeutic strategy for treating cardiac hypertrophy, an important risk factor for subsequent cardiac morbidity and mortality. However, the lack of safe and efficient in vivo delivery of siRNAs is a major challenge for broadening its clinical applications. Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) are a promising delivery system for siRNAs but have limited cell/tissue-specific targeting ability. In this study, a new generation of heart-targeting sEVs (CEVs) has been developed by conjugating cardiac-targeting peptide (CTP) to human peripheral blood-derived sEVs (PB-EVs), using a simple, rapid and scalable method based on bio-orthogonal copper-free click chemistry. The experimental results show that CEVs have typical sEVs properties and excellent heart-targeting ability. Furthermore, to treat cardiac hypertrophy, CEVs are loaded with NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) siRNA (siNOX4). Consequently, CEVs@siNOX4 treatment enhances the in vitro anti-hypertrophic effects by CEVs with siRNA protection and heart-targeting ability. In addition, the intravenous injection of CEVs@siNOX4 into angiotensin II (Ang II)-treated mice significantly improves cardiac function and reduces fibrosis and cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area, with limited side effects. In conclusion, the utilization of CEVs represents an efficient strategy for heart-targeted delivery of therapeutic siRNAs and holds great promise for the treatment of cardiac hypertrophy.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase 4; cardiac hypertrophy; cardiac-targeting peptide; small extracellular vesicles; small-interfering RNA.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez‐Erviti, L. , Seow, Y. , Yin, H. , Betts, C. , Lakhal, S. , & Wood, M. J. (2011). Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nature biotechnology, 29(4), 341–345. - PubMed
-
- Avula, U. M. , Yoon, H. K. , Lee, C. H. , Kaur, K. , Ramirez, R. J. , Takemoto, Y. , Ennis, S. R. , Morady, F. , Herron, T. , Berenfeld, O. , Kopelman, R. , & Kalifa, J. (2015). Cell‐selective arrhythmia ablation for photomodulation of heart rhythm. Science Translational Medicine, 7(311), 311ra172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

