Recurring Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor: Timing and Pattern of Recurrence and Current Treatment
- PMID: 37796750
- PMCID: PMC10556340
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005809
Recurring Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor: Timing and Pattern of Recurrence and Current Treatment
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to describe the pattern of recurrence, treatments received, as well the oncological outcomes, of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) following curative surgery.
Background: PanNETs recur in 10% to 15% of cases following surgery. Information on the natural history and management of recurring disease is lacking.
Materials and methods: Patients with PanNET that underwent curative surgery at 4 institutions between 2000 and 2019 were identified. Patients with poorly differentiated tumors, unknown tumor grade and differentiation, hereditary syndromes, unknown margin or R2 status, metastatic, and those that had neoadjuvant treatment or perioperative mortality were excluded. Clinical variables were assessed including first site of recurrence, treatment received, and survival outcomes.
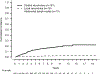
Results: A total of 1402 patients were included: 957 (74%) had grade 1, 322 (25%) had grade 2, and 13 (1%) had grade 3 tumors. Median follow-up was 4.8 years (interquartile range: 2-8.2 years). Cumulative incidence of recurrence at 5 years was 13% (95% CI: 11%-15.2%) for distant disease, 1.4% (95% CI: 0.8%-2.3%) for locoregional recurrence, and 0.8% (95% CI: 0.4%-1.5%) for abdominal nodal recurrence. Patients who recurred had 2.89 increased risk of death (95% CI: 2-4.1) as compared with patients who did not recur. Therapy postrecurrence included: somatostatin analogs in 111 (61.0%), targeted therapies in 48 (26.4%), liver-directed therapies in 61 (33.5%), peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in 30 (16.5%), and surgery in 46 (25.3%) patients. Multiple treatments were used in 103 (57%) cases. After the first recurrence, 5-year overall survival was 74.6% (95% CI: 67.4%-82.5%).
Conclusions: Recurrence following surgery is infrequent but reduces survival. Most recurrences are distant and managed with multiple therapies. Prospective studies are needed to establish strategies for surveillance and the sequence of treatment to control the disease and prolong survival.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
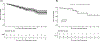

References
-
- Marchegiani G, Landoni L, Andrianello S, et al. Patterns of recurrence after resection for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: who, when, and where? Neuroendocrinology. 2018; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

