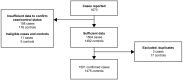
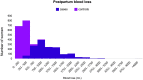
Postpartum haemorrhage occurring in UK midwifery units: A national population-based case-control study to investigate incidence, risk factors and outcomes
- PMID: 37796876
- PMCID: PMC10553245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291795
Postpartum haemorrhage occurring in UK midwifery units: A national population-based case-control study to investigate incidence, risk factors and outcomes
Abstract
Objectives: To estimate the incidence of, and investigate risk factors for, postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) requiring transfer to obstetric care following birth in midwifery units (MU) in the UK; to describe outcomes for women who experience PPH requiring transfer to obstetric care.
Methods: We conducted a national population-based case-control study in all MUs in the UK using the UK Midwifery Study System (UKMidSS). Between September 2019 and February 2020, 1501 women with PPH requiring transfer to obstetric care following birth in an MU, and 1475 control women were identified. We used multivariable logistic regression, generating adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to investigate risk factors for PPH requiring transfer to obstetric care.
Results: The incidence of PPH requiring transfer to obstetric care following birth in an MU was 3.7% (95% CI 3.6%-3.9%). Factors independently associated with PPH requiring transfer to obstetric care were smoking during pregnancy (aOR = 0.73; 95% CI 0.56-0.94), nulliparity (aOR = 1.96; 95% CI 1.66-2.30), previous PPH (aOR = 2.67; 95% CI 1.67-4.25), complications in a previous pregnancy other than PPH (aOR = 2.40; 95% CI 1.25-4.60), gestational age ≥41 weeks (aOR = 1.36; 95% CI 1.10-1.69), instrumental birth (aOR = 2.69; 95% CI 1.53-4.72), third stage of labour ≥60 minutes (aOR = 5.56; 95% CI 3.93-7.88), perineal trauma (aOR = 4.67; 95% CI 3.16-6.90), and birthweight 3500-3999g (aOR = 1.71; 95% CI 1.42-2.07) or ≥4000g (aOR = 2.31; 95% CI 1.78-3.00). One in ten (10.6%) cases received a blood transfusion and one in five (21.0%) were admitted to higher level care.
Conclusions: The risk factors identified in this study align with those identified in previous research and with current guidelines for women planning birth in an MU in the UK. Maternal outcomes after PPH were broadly reassuring and indicative of appropriate management. NHS organisations should ensure that robust guidelines are in place to support management of PPH in MUs.
Copyright: © 2023 Elkington et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- NMPA. National Maternity and Perinatal Audit: Clinical Report 2017. London; 2017.
-
- Department of Health. Changing childbirth: Part I: Report of the Expert Maternity Group. London: HMSO; 1993.
-
- (NICE) NIfHaCE. Intrapartum Care: Care of Healthy Women and their Babies During Childbirth. London; 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials