RECOVER identifies synergistic drug combinations in vitro through sequential model optimization
- PMID: 37797618
- PMCID: PMC10626197
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100599
RECOVER identifies synergistic drug combinations in vitro through sequential model optimization
Abstract
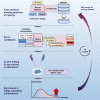
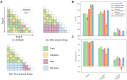
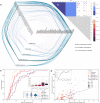
For large libraries of small molecules, exhaustive combinatorial chemical screens become infeasible to perform when considering a range of disease models, assay conditions, and dose ranges. Deep learning models have achieved state-of-the-art results in silico for the prediction of synergy scores. However, databases of drug combinations are biased toward synergistic agents and results do not generalize out of distribution. During 5 rounds of experimentation, we employ sequential model optimization with a deep learning model to select drug combinations increasingly enriched for synergism and active against a cancer cell line-evaluating only ∼5% of the total search space. Moreover, we find that learned drug embeddings (using structural information) begin to reflect biological mechanisms. In silico benchmarking suggests search queries are ∼5-10× enriched for highly synergistic drug combinations by using sequential rounds of evaluation when compared with random selection or ∼3× when using a pretrained model.
Keywords: CP: Systems biology; active learning; deep learning; drug combination; drug synergy; in vitro screening; machine learning; oncology; sequential model optimization.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests All authors affiliated with Relation Therapeutics receive equity-based compensation in the company. N.V. holds stock in Glyde Bio, Inc., and Innovac Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Tyers M., Wright G.D. Drug combinations: a strategy to extend the life of antibiotics in the 21st century. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019;17:141–155. - PubMed
-
- Al-Lazikani B., Banerji U., Workman P. Combinatorial drug therapy for cancer in the post-genomic era. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:679–692. - PubMed
-
- Janes J., Young M.E., Chen E., Rogers N.H., Burgstaller-Muehlbacher S., Hughes L.D., Love M.S., Hull M.V., Kuhen K.L., Woods A.K., et al. The reframe library as a comprehensive drug repurposing library and its application to the treatment of cryptosporidiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:10750–10755. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

