Single-cell analysis reveals altered tumor microenvironments of relapse- and remission-associated pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 37798266
- PMCID: PMC10556066
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41994-0
Single-cell analysis reveals altered tumor microenvironments of relapse- and remission-associated pediatric acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
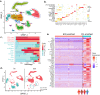
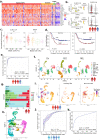
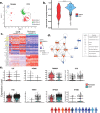
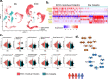
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) microenvironment exhibits cellular and molecular differences among various subtypes. Here, we utilize single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to analyze pediatric AML bone marrow (BM) samples from diagnosis (Dx), end of induction (EOI), and relapse timepoints. Analysis of Dx, EOI scRNA-seq, and TARGET AML RNA-seq datasets reveals an AML blasts-associated 7-gene signature (CLEC11A, PRAME, AZU1, NREP, ARMH1, C1QBP, TRH), which we validate on independent datasets. The analysis reveals distinct clusters of Dx relapse- and continuous complete remission (CCR)-associated AML-blasts with differential expression of genes associated with survival. At Dx, relapse-associated samples have more exhausted T cells while CCR-associated samples have more inflammatory M1 macrophages. Post-therapy EOI residual blasts overexpress fatty acid oxidation, tumor growth, and stemness genes. Also, a post-therapy T-cell cluster associated with relapse samples exhibits downregulation of MHC Class I and T-cell regulatory genes. Altogether, this study deeply characterizes pediatric AML relapse- and CCR-associated samples to provide insights into the BM microenvironment landscape.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
M.B. serves on the board of Canomiks Inc. as chief scientific advisor and has equity in it. D.K.G. and D.D. hold equity in Meryx Inc. S.S.B. serves as CEO of Anxomics LLC and has equity in it. The remaining authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Egan G, Chopra Y, Mourad S, Chiang KY, Hitzler J. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia in children: a practical perspective. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2021;68:e28979. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

