No phenotypic or genotypic evidence for a link between sleep duration and brain atrophy
- PMID: 37798367
- PMCID: PMC10663160
- DOI: 10.1038/s41562-023-01707-5
No phenotypic or genotypic evidence for a link between sleep duration and brain atrophy
Abstract
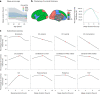
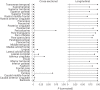
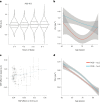
Short sleep is held to cause poorer brain health, but is short sleep associated with higher rates of brain structural decline? Analysing 8,153 longitudinal MRIs from 3,893 healthy adults, we found no evidence for an association between sleep duration and brain atrophy. In contrast, cross-sectional analyses (51,295 observations) showed inverse U-shaped relationships, where a duration of 6.5 (95% confidence interval, (5.7, 7.3)) hours was associated with the thickest cortex and largest volumes relative to intracranial volume. This fits converging evidence from research on mortality, health and cognition that points to roughly seven hours being associated with good health. Genome-wide association analyses suggested that genes associated with longer sleep for below-average sleepers were linked to shorter sleep for above-average sleepers. Mendelian randomization did not yield evidence for causal impacts of sleep on brain structure. The combined results challenge the notion that habitual short sleep causes brain atrophy, suggesting that normal brains promote adequate sleep duration-which is shorter than current recommendations.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.E.S. reports consulting fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals and is now a full-time employee of the US Alzheimer’s Association. C.A.D. is a cofounder, stock owner, board member and consultant in the contract laboratory Vitas AS, performing personalized analyses of blood biomarkers. The rest of the authors report no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

