Engeletin alleviates depression-like phenotype by increasing synaptic plasticity via the BDNF-TrkB-mTORC1 signalling pathway
- PMID: 37799103
- PMCID: PMC10718134
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17975
Engeletin alleviates depression-like phenotype by increasing synaptic plasticity via the BDNF-TrkB-mTORC1 signalling pathway
Abstract
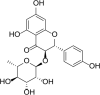
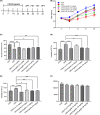
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a severe mental disorder associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality. Current first-line pharmacotherapies for MDD are based on enhancement of monoaminergic neurotransmission, but these antidepressants are still insufficient and produce significant side-effects. Consequently, the development of novel antidepressants and therapeutic targets is desired. Engeletin, a natural Smilax glabra rhizomilax derivative, is a compound with proven efficacy in treating ischemic stroke, yet its therapeutic effects and mechanisms for depression remain unexplored. The effects of engeletin were assessed in the forced swimming test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST) in mice. Engeletin was also investigated in the chronic restraint stress (CRS) mouse model of depression with fluoxetine (FLX) as the positive control. Changes in prefrontal cortex (PFC) spine density, synaptic plasticity-linked protein expressions and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-tyrosine kinase B (TrkB)- mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signalling pathway after chronic stress and engeletin treatment were then investigated. The TrkB and mTORC1 selective inhibitors, ANA-12 and rapamycin, respectively, were utilized to assess the engeletin's antidepressive mechanisms. Our data shows that engeletin exhibited antidepressant-like activity in the FST and TST in mice without affecting locomotor activity. Furthermore, it exhibited efficiency against the depression of CRS model. Moreover, it enhanced the BDNF-TrkB-mTORC1 pathway in the PFC during CRS and altered the reduction in dendritic spine density and levels of synaptic plasticity-linked protein induced by CRS. In conclusion, engeletin has antidepressant activity via activation of the BDNF-TrkB-mTORC1 signalling pathway and upregulation of PFC synaptic plasticity.
Keywords: BDNF-TrkB-mTORC1 signalling pathway; chronic restraint stress; engeletin; major depressive disorder; prefrontal cortex; synaptic plasticity.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Isoflurane produces antidepressant effects inducing BDNF-TrkB signaling in CUMS mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Nov;236(11):3301-3315. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05287-z. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31197433
-
Rapid antidepressant-like effects of muscarinic receptor antagonists require BDNF-dependent signaling in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Dec;239(12):3805-3818. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06250-1. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36221037
-
Licorisoflavan A Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice: Involvement of BDNF-TrkB Pathway and AMPA Receptors.Neurochem Res. 2019 Sep;44(9):2044-2056. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02840-2. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 31278631
-
Role of BDNF-mTORC1 Signaling Pathway in Female Depression.Neural Plast. 2021 Feb 9;2021:6619515. doi: 10.1155/2021/6619515. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 33628219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid-acting antidepressants and the regulation of TrkB neurotrophic signalling-Insights from ketamine, nitrous oxide, seizures and anaesthesia.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Aug;129(2):95-103. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13598. Epub 2021 May 24. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33973360 Review.
Cited by
-
Bergamot essential oil improves CUMS-induced depression-like behaviour in rats by protecting the plasticity of hippocampal neurons.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(8):e18178. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18178. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38553964 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine in depression: focused on the modulation of neuroplasticity.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 26;15:1426769. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1426769. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39253375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engeletin alleviates depressive-like behaviours by modulating microglial polarization via the LCN2/CXCL10 signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(8):e18285. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18285. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38597406 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Pathogenesis of Post-stroke Depression.Aging Dis. 2024 Feb 9;16(1):209-38. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0203. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38377025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Late-onset major depressive disorder: exploring the therapeutic potential of enhancing cerebral brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression through targeted microRNA delivery.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):352. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02935-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39227372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiba S, Numakawa T, Ninomiya M, Richards MC, Wakabayashi C, Kunugi H. Chronic restraint stress causes anxiety‐ and depression‐like behaviors, downregulates glucocorticoid receptor expression, and attenuates glutamate release induced by brain‐derived neurotrophic factor in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2012;39(1):112‐119. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.05.018 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017WS153/Project of Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan
- 202209010908/Project of Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan
- BY2016KJ11/Binzhou Medical University Science and Technology Program
- BY2020KJ43/Binzhou Medical University Science and Technology Program
- 31570352/National Natural Science Foundation of China - State Grid Corporation Joint Fund for Smart Grid
- 31170321/National Natural Science Foundation of China - State Grid Corporation Joint Fund for Smart Grid
- Q-2023011/Shandong Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology Project
- 2019JZZY011122/The Key "Major New Drugs Research & Development" Project of Shandong Province
- 2021XDHZ081/Yantai science and technology plan project
- 2020XFRH109/Yantai science and technology plan project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

