Fractal dimension analysis of resting state functional networks in schizophrenia from EEG signals
- PMID: 37799187
- PMCID: PMC10547874
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1236832
Fractal dimension analysis of resting state functional networks in schizophrenia from EEG signals
Abstract
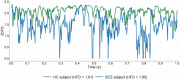
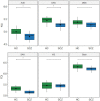
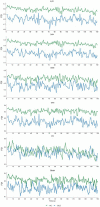
Fractal dimension (FD) has been revealed as a very useful tool in analyzing the changes in brain dynamics present in many neurological disorders. The fractal dimension index (FDI) is a measure of the spatiotemporal complexity of brain activations extracted from EEG signals induced by transcranial magnetic stimulation. In this study, we assess whether the FDI methodology can be also useful for analyzing resting state EEG signals, by characterizing the brain dynamic changes in different functional networks affected by schizophrenia, a mental disorder associated with dysfunction in the information flow dynamics in the spontaneous brain networks. We analyzed 31 resting-state EEG records of 150 s belonging to 20 healthy subjects (HC group) and 11 schizophrenia patients (SCZ group). Brain activations at each time sample were established by a thresholding process applied on the 15,002 sources modeled from the EEG signal. FDI was then computed individually in each resting-state functional network, averaging all the FDI values obtained using a sliding window of 1 s in the epoch. Compared to the HC group, significant lower values of FDI were obtained in the SCZ group for the auditory network (p < 0.05), the dorsal attention network (p < 0.05), and the salience network (p < 0.05). We found strong negative correlations (p < 0.01) between psychopathological scores and FDI in all resting-state networks analyzed, except the visual network. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis also revealed that the FDI of the salience network performed very well as a potential feature for classifiers of schizophrenia, obtaining an area under curve value of 0.83. These results suggest that FDI is a promising method for assessing the complexity of the brain dynamics in different regions of interest, and from long resting-state EEG signals. Regarding the specific changes associated with schizophrenia in the dynamics of the spontaneous brain networks, FDI distinguished between patients and healthy subjects, and correlated to clinical variables.
Keywords: EEG; fractal dimension; functional network; resting state; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2023 Ruiz de Miras, Ibáñez-Molina, Soriano and Iglesias-Parro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Spatio-Temporal Fractal Dimension Analysis from Resting State EEG Signals in Parkinson's Disease.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Jul 2;25(7):1017. doi: 10.3390/e25071017. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509964 Free PMC article.
-
Fractal dimension analysis of states of consciousness and unconsciousness using transcranial magnetic stimulation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Jul;175:129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31104702
-
Analysis of functional connectivity using machine learning and deep learning in different data modalities from individuals with schizophrenia.J Neural Eng. 2023 Sep 28;20(5). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acf734. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 37673060
-
Using resting state functional connectivity to unravel networks of tinnitus.Hear Res. 2014 Jan;307:153-62. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Hear Res. 2014. PMID: 23895873 Review.
-
Mapping cognitive and emotional networks in neurosurgical patients using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging.Neurosurg Focus. 2020 Feb 1;48(2):E9. doi: 10.3171/2019.11.FOCUS19773. Neurosurg Focus. 2020. PMID: 32006946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic Evolution of EEG Complexity in Schizophrenia Across Cognitive Tasks.Entropy (Basel). 2025 Feb 22;27(3):226. doi: 10.3390/e27030226. Entropy (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40149150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksentijevic A., Mihailović A., Mihailović D. T. (2021). A novel approach to the study of spatio-temporal brain dynamics using change-based complexity. Appl. Math. Comput. 410:126432. doi: 10.1016/J.AMC.2021.126432 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

