Treatment of a Non-syndromic Carotid Body Paraganglioma Using Fast Neutron Radiotherapy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- PMID: 37799247
- PMCID: PMC10550357
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44673
Treatment of a Non-syndromic Carotid Body Paraganglioma Using Fast Neutron Radiotherapy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
Non-syndromic carotid body paragangliomas (CBPs) are the most common head and neck CBPs. Malignant transformation or symptomatic presentation is rare, but patients may occasionally endorse tinnitus, cranial nerve (CN) deficits, and ear pulsations. Historically, treatment of CBP was primarily through surgical intervention, which predisposed patients to CN deficits and significant blood loss due to the neurovascular structures in close proximity to these tumors. More recently, the utilization of pre-treatment embolization and radiotherapy has allowed for the reduction in treatment morbidity. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) have been investigated as alternatives to traditional surgical intervention, with a documented reduction in the incidence of postoperative morbidity. While several retrospective studies and meta-analyses compare outcomes following surgical and traditional radiotherapeutic interventions, currently no literature exists regarding the potential utility of fast neutron therapy in treating this disease. In this case report, we highlight a patient with a non-syndromic CBP treated with pre-treatment embolization and fast neutron therapy, review the post-treatment course, and present a review of the extant literature on the subject.
Keywords: carotid body paraganglioma; glomus tumor; neutron therapy; pre-treatment embolization; radiation therapy.
Copyright © 2023, Ramanathan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
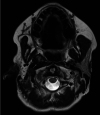
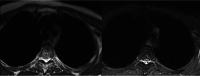
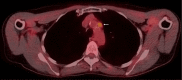
Similar articles
-
Jugular and vagal paragangliomas: Systematic study of management with surgery and radiotherapy.Head Neck. 2013 Aug;35(8):1195-204. doi: 10.1002/hed.22976. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Head Neck. 2013. PMID: 22422597 Review.
-
Paragangliomas of the head and neck.J Oral Pathol Med. 2022 Nov;51(10):897-903. doi: 10.1111/jop.13286. Epub 2022 Feb 23. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022. PMID: 35178777 Review.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery for head and neck paragangliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2021 Apr;44(2):741-752. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01292-5. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Neurosurg Rev. 2021. PMID: 32318920
-
Long-term results of irradiation for paraganglioma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Jul 15;65(4):1063-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.02.020. Epub 2006 May 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 16682153
-
Giant carotid chemodectoma treated with a combination of surgery and CyberKnife radiotherapy: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2022 Feb 25;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-03237-y. J Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35216640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Paragangliomas of the Head and Neck: A Review of the Latest Diagnostic and Treatment Methods.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 30;60(6):914. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060914. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Galan SR, Kann PH. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013;78:165–175. - PubMed
-
- Important observations made managing carotid body tumors during a 25-year experience. Kruger AJ, Walker PJ, Foster WJ, Jenkins JS, Boyne NS, Jenkins J. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:1518–1523. - PubMed
-
- Early side effects after embolization of a carotid body tumor using Onyx. Wiegand S, Kureck I, Chapot R, Sesterhenn AM, Bien S, Werner JA. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:742–745. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
