The decoy oligodeoxynucleotide against HIF-1α and STAT5 ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like mouse model
- PMID: 37799329
- PMCID: PMC10550406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102036
The decoy oligodeoxynucleotide against HIF-1α and STAT5 ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like mouse model
Abstract
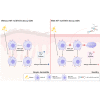
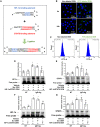
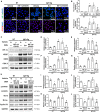
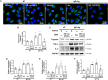
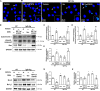
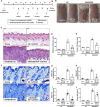
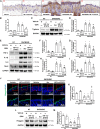
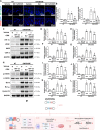
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common inflammatory skin disease caused by an immune disorder. Mast cells are known to be activated and granulated to maintain an allergic reaction, including rhinitis, asthma, and AD. Although hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) play crucial roles in mast cell survival and granulation, their effects need to be clarified in allergic disorders. Thus, we designed decoy oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) synthetic DNA, without open ends, containing complementary sequences for HIF-1α and STAT5 to suppress the transcriptional activities of HIF-1α and STAT5. In this study, we demonstrated the effects of HIF-1α/STAT5 ODN using AD-like in vivo and in vitro models. The HIF-1α/STAT5 decoy ODN significantly alleviated cutaneous symptoms similar to AD, including morphology changes, immune cell infiltration, skin barrier dysfunction, and inflammatory response. In the AD model, it also inhibited mast cell infiltration and degranulation in skin tissue. These results suggest that the HIF-1α/STAT5 decoy ODN ameliorates the AD-like disorder and immunoglobulin E (IgE)-induced mast cell activation by disrupting HIF-1α/STAT5 signaling pathways. Taken together, these findings suggest the possibility of HIF-1α/STAT5 as therapeutic targets and their decoy ODN as a potential therapeutic tool for AD.
Keywords: HIF-1α; MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; STAT5; atopic dermatitis; decoy oligodeoxynucleotide; mast cell.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo transfection of a cis element 'decoy' against signal transducers and activators of transcription 6 (STAT6)-binding site ameliorates IgE-mediated late-phase reaction in an atopic dermatitis mouse model.Gene Ther. 2004 Dec;11(24):1753-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302341. Gene Ther. 2004. PMID: 15306842
-
HIF-1α decoy oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit HIF-1α signaling and breast cancer proliferation.Int J Oncol. 2015 Jan;46(1):215-22. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2715. Epub 2014 Oct 21. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25334080
-
[Targeted blockage of STAT5 by a decoy oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits the growth and proliferation of K562 cells].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Dec;25(12):724-7. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15730714 Chinese.
-
Decoy oligodeoxynucleotides: A promising therapeutic strategy for inflammatory skin disorders.Hum Immunol. 2024 Nov;85(6):111161. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2024.111161. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Hum Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39454315 Review.
-
IgE, mast cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Dec;41(3):298-310. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8252-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21249468 Review.
Cited by
-
Kahweol Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Tumor Necrosis Factor-α/Interferon-γ-Stimulated Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Apr 18;46(4):3470-3483. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040218. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666948 Free PMC article.
-
Amplified Production of a DNA Decoy Catalyzed by Intracellular MicroRNA.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Apr 7;64(15):e202424421. doi: 10.1002/anie.202424421. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39901657 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the research frontier of hypoxia in skin health and diseases: a bibliometric analysis.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 May 29;87(8):4949-4962. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003303. eCollection 2025 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40787562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asher M.I., Montefort S., Björkstén B., Lai C.K.W., Strachan D.P., Weiland S.K., Williams H., ISAAC Phase Three Study Group Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368:733–743. - PubMed
-
- Lim J.Y., Lee J.H., Lee D.H., Lee J.H., Kim D.K. Umbelliferone reduces the expression of inflammatory chemokines in HaCaT cells and DNCB/DFE-induced atopic dermatitis symptoms in mice. Int. Immunopharm. 2019;75 - PubMed
-
- Flohr C., Mann J. New insights into the epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2014;69:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Drube S., Grimlowski R., Deppermann C., Fröbel J., Kraft F., Andreas N., Stegner D., Dudeck J., Weber F., Rödiger M., et al. The Neurobeachin-like 2 Protein Regulates Mast Cell Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2017;199:2948–2957. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

