The complete chloroplast genome of Scutellaria barbata D. Don 1825 revealed the phylogenetic relationships of the Scutellaria genus
- PMID: 37799449
- PMCID: PMC10548842
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2023.2261564
The complete chloroplast genome of Scutellaria barbata D. Don 1825 revealed the phylogenetic relationships of the Scutellaria genus
Abstract
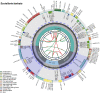
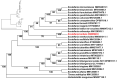
Scutellaria barbata D. Don 1825 is an important medicinal plant distributed in wetlands about 2000 m above sea level and used to treat various diseases. The complete chloroplast genome of S. barbata is 152,050 bp with four subregions consisting of a large single-copy region (84,053 bp), a small single-copy region (17,517 bp), and a pair of inverted repeats (25,240 bp). In the chloroplast genome of S. barbata, 131 genes were detected, comprising 87 protein-encoding genes, eight ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes, and 36 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes. Phylogenetic analysis based on the complete chloroplast genome and protein-coding DNA sequences of 27 related taxa of the genus (out group included Holmskioldia sanguinea and Tinnea aethiopica) indicates that S. barbata was made a clade with S. orthocalyx, and S. meehanioides was a sister to them. The first chloroplast genome of S. barbata was reported in this work, serving as a potential reference for important medicinal plants within the Scutellaria genus.
Keywords: Chloroplast genome; Scutellaria barbata; phylogenetic relationships.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Bruno M, Piozzi F, Maggio AM, Simmonds MS.. 2002. Antifeedant activity of neoclerodane diterpenoids from two Sicilian species of Scutellaria. Biochem Syst Ecol. 30(8):793–799. doi: 10.1016/S0305-1978(01)00143-0. - DOI
-
- Chen S. 2019. Genetic and phylogenetic analysis of the complete genome for the herbal medicine plant of Scutellaria baicalensis from China. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 4(1):1683–1685. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1605859. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
