Determining the reliability of diagnosis and treatment using artificial intelligence software with panoramic radiographs
- PMID: 37799743
- PMCID: PMC10548159
- DOI: 10.5624/isd.20230109
Determining the reliability of diagnosis and treatment using artificial intelligence software with panoramic radiographs
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and effectiveness of an artificial intelligence (AI) program in identifying dental conditions using panoramic radiographs (PRs), as well as to assess the appropriateness of its treatment recommendations.
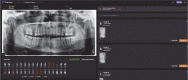
Material and methods: PRs from 100 patients (representing 4497 teeth) with known clinical examination findings were randomly selected from a university database. Three dentomaxillofacial radiologists and the Diagnocat AI software evaluated these PRs. The evaluations were focused on various dental conditions and treatments, including canal filling, caries, cast post and core, dental calculus, fillings, furcation lesions, implants, lack of interproximal tooth contact, open margins, overhangs, periapical lesions, periodontal bone loss, short fillings, voids in root fillings, overfillings, pontics, root fragments, impacted teeth, artificial crowns, missing teeth, and healthy teeth.
Results: The AI demonstrated almost perfect agreement (exceeding 0.81) in most of the assessments when compared to the ground truth. The sensitivity was very high (above 0.8) for the evaluation of healthy teeth, artificial crowns, dental calculus, missing teeth, fillings, lack of interproximal contact, periodontal bone loss, and implants. However, the sensitivity was low for the assessment of caries, periapical lesions, pontic voids in the root canal, and overhangs.
Conclusion: Despite the limitations of this study, the synthesized data suggest that AI-based decision support systems can serve as a valuable tool in detecting dental conditions, when used with PR for clinical dental applications.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Deep Learning; Dentistry; Radiography, Panoramic.
Copyright © 2023 by Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no disclosures to report regarding funding, disclaimer statements, presentations of the research at conferences or symposia, or postings of the work on a preprint server, website, or other location. Kaan Orhan serves as a Scientific Advisor for Diagnocat Inc., based in San Francisco, CA, USA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence Software in Identifying Common Periodontal and Restorative Dental Conditions (Marginal Bone Loss, Periapical Lesion, Crown, Restoration, Dental Caries) in Intraoral Periapical Radiographs.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 4;15(11):1432. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111432. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507004 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic charting of panoramic radiography using deep-learning artificial intelligence system.Oral Radiol. 2022 Jul;38(3):363-369. doi: 10.1007/s11282-021-00572-0. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Oral Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34611840
-
Evaluation of Dental Panoramic Radiographs by Artificial Intelligence Compared to Human Reference: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 14;13(22):6859. doi: 10.3390/jcm13226859. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39598002 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis on Two-Dimensional Radiographs: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 15;59(4):768. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040768. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of periodontal bone loss and periodontitis from 2D dental radiographs via machine learning and deep learning: systematic review employing APPRAISE-AI and meta-analysis.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2025 Feb 1;54(2):89-108. doi: 10.1093/dmfr/twae070. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39656957 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of Treatment Recommendations by Pragmatic Evidence Search and Artificial Intelligence: An Exploratory Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;14(5):527. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14050527. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38472998 Free PMC article.
-
Auxiliary Diagnosis of Dental Calculus Based on Deep Learning and Image Enhancement by Bitewing Radiographs.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;11(7):675. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11070675. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061757 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Diagnostic Accuracy of an AI-Driven Platform for Assessing Endodontic Treatment Outcomes Using Panoramic Radiographs: A Preliminary Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Jun 11;13(12):3401. doi: 10.3390/jcm13123401. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38929931 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Age Estimation from OPG Images and Patient Records Using Deep Feature Extraction and Modified Genetic-Random Forest.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;15(3):314. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15030314. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941244 Free PMC article.
-
Concerns regarding deployment of AI-based applications in dentistry - a review.BDJ Open. 2025 Mar 25;11(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41405-025-00319-7. BDJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40133287 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chartrand G, Cheng PM, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal CJ, et al. Deep learning: a primer for radiologists. Radiographics. 2017;37:2113–2131. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, MacKinnon T. Artificial intelligence in fracture detection: transfer learning from deep convolutional neural networks. Clin Radiol. 2018;73:439–445. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

