Anomalous photochromism and mechanochromism of a linear naphthopyran enabled by a polarizing dialkylamine substituent
- PMID: 37800007
- PMCID: PMC10548511
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc03790h
Anomalous photochromism and mechanochromism of a linear naphthopyran enabled by a polarizing dialkylamine substituent
Abstract
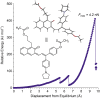
In contrast to common angular naphthopyrans that exhibit strong photochromic and mechanochromic behavior, constitutionally isomeric linear naphthopyrans are typically not photochromic, due to the putative instability of the completely dearomatized merocyanine product. The photochemistry of linear naphthopyrans is thus relatively understudied compared to angular naphthopyrans, while the mechanochromism of linear naphthopyrans remains completely unexplored. Here we demonstrate that the incorporation of a polarizing dialkylamine substituent enables photochromic and mechanochromic behavior from polymers containing a novel linear naphthopyran motif. In solution phase experiments, a Lewis acid trap was necessary to observe accumulation of the merocyanine product upon photochemical and ultrasound-induced mechanochemical activation. However, the same linear naphthopyran molecule incorporated as a crosslinker in polydimethylsiloxane elastomers renders the materials photochromic and mechanochromic without the addition of any trapping agent. This study provides insights into the photochromic and mechanochromic reactivity of linear naphthopyrans that have conventionally been considered functionally inert, adding a new class of naphthopyran molecular switches to the repertoire of stimuli-responsive polymers.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Hepworth J. D. and Heron B. M., in Functional Dyes, Elsevier Science, 2006, pp. 85–135
-
- Van Gemert B., in Organic Photochromic and Thermochromic Compounds, Springer, Boston, MA, 2002, pp. 111–140
-
- Corns S. N. Partington S. M. Towns A. D. Color. Technol. 2009;125:249–261.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

