How Nurses' Person-Organization Fit Influences Organizational Loyalty
- PMID: 37800114
- PMCID: PMC10547909
- DOI: 10.2147/RMHP.S425025
How Nurses' Person-Organization Fit Influences Organizational Loyalty
Abstract
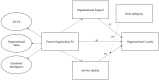
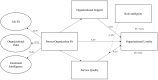
Background: High turnover rates among nurses are a global concern due to the shortage of skilled professionals and increasing demand for high-quality healthcare. This study aims to enhance understanding of organizational fit by examining the impact of Person-organization fit (P-O fit) on organizational loyalty through the mediating role of organizational support and service quality, and the moderating impact of role ambiguity.
Methods: Using a convenience sampling technique, we employed a survey methodology by developing a questionnaire. Data were collected from a sample of 614 nurses in five different healthcare sectors in China. Employing SmartPLS 3.3, we conducted a Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis to examine the relationships among the specified variables.
Results: The findings of the structural analysis suggest that the P-O fit influences organizational loyalty in the healthcare sector. Organizational support and service quality were identified as partial mediators of the P-O fit-organizational loyalty link. Additionally, the role of ambiguity represented a negative moderating impact between service quality and organizational loyalty.
Discussion: Overall, the study's findings extend the understanding of person-organization fit, organizational support, service quality, role ambiguity, and organizational loyalty in the context of healthcare sectors and offer implications for medical authorities. Discussions, limitations, practical implications, and suggestions for further research are also provided.
Keywords: organizational loyalty; organizational support; person-organization fit; role ambiguity; service quality.
© 2023 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources