Impact of Baricitinib on Patients' Quality of Life after One Year of Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis in Real-World Practice: Results of the Observatory of Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases Registry
- PMID: 37800349
- PMCID: PMC10566517
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v103.14153
Impact of Baricitinib on Patients' Quality of Life after One Year of Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis in Real-World Practice: Results of the Observatory of Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases Registry
Abstract
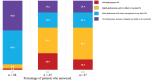
The efficacy and safety of baricitinib for treatment of atopic dermatitis have been demonstrated in clinical trials; however, very few real-life studies have been published to date. The Observatory of Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases (OMCCI) registry was initiated to prospectively determine the long-term impairment caused by chronic inflammatory dermatoses on patients' lives. The study included 88 patients starting baricitinib for treatment of atopic dermatitis. Clinical evaluation and patient-reported outcomes were recorded at baseline and after 6 and 12 months. After 6 months and 1 year of follow-up, 65 and 47 patients, respectively, were still being treated with baricitinib. Treatment failure was the main reason for discontinuation. Only 1 patient stopped baricitinib because of a side-effect. After 1 year of follow-up, the mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score decreased significantly from 20.7 to 6.4; the percentage of patients with severe atopic dermatitis decreased from 42.9% to 6.5% and a significant improvement in most patient-reported outcomes was noted. There was no difference in terms of efficacy whether or not patients were previously treated with dupilumab. The results remained stable after 6 and 12 months of treatment, which suggests a sustained efficacy of the treatment in patients who initially responded well.
Conflict of interest statement
ZR has received consulting fees and honoraria from: Abbvie, Almirall, Amgen, Avene, BMS, Celgene, GSK, Janssen-Cilag, Leo-Pharma, Lilly, Medac, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre Dermatologie, Pfizer, UCB, Sanofi. Investigator for: AbbVie, Actelion, Almirall, Amgen, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, BMS, Forward Pharma, GSK, Galderma, Genentec, Incyte, Janssen Cilag, Leo-Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Regeneron, UCB, Sanofi. PAB has received consultant and/or member of boards and/or speaker fees from: AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Léo-pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, UCB. JLP has received consultant fees from: Sanofi, Lilly, Leo, Pharma, Pfizer. A-CF has received speaker, consultant or investigator fees from: AbbVie, Leo-Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi. EB: Lilly, AbbVie, UCB, Novartis, Sanofi, Janssen. CB: AbbVie, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, UCB, Lilly, Almirall. CF: AbbVie, Sanofi, Janssen, UCB, Novartis, Almirall, Lilly. IZ: AbbVie, Novatis, Lilly, Leo, Sanofi, UCB, Janssen, Almirall. DL-D: AbbVie, Almirall, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Sanofi, UCB. A-LL: Novartis, Janssen, UCB, AbbVie. JP: Leo, Amgen, UCB, Almirall, Janssen, AbbVie, Novartis, Medac, Lilly, Sanofi. NQ-T: AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Janssen Cilag, Léo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis. FM has received consulting fees from: Almirall, AbbVie, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi. GC: Abbvie, Pfizer, Janssen, UCB. CP and LD have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Richard MA, Corgibet F, Beylot-Barry M, Barbaud A, Bodemer C, Chaussade V, et al. . Sex- and age-adjusted prevalence estimates of five chronic inflammatory skin diseases in France: results of the “Objectifs Peau” study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2018; 32: 1967–1971. - PubMed
-
- Barbarot S, Auziere S, Gadkari A, Girolomoni G, Puig L, Simpson EL, et al. . Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: results from an international survey. Allergy 2018; 73: 1284–1293. - PubMed
-
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Eckert L, Wu R, Ardeleanu M, Graham NM, et al. . Patient burden of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD): insights from a phase 2b clinical trial of dupilumab in adults. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016; 74: 491–498. - PubMed
-
- Eckert L, Gupta S, Amand C, Gadkari A, Mahajan P, Gelfand JM. The burden of atopic dermatitis in US adults: health care resource utilization data from the 2013 National Health and Wellness Survey. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018; 78: 54–61.e1. - PubMed
-
- Simpson EL, Lacour JP, Spelman L, Galimberti R, Eichenfield LF, Bissonnette R, et al. . Baricitinib in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis and inadequate response to topical corticosteroids: results from two randomized monotherapy phase III trials. Br J Dermatol 2020; 183: 242–255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

