Climate change and its influence in nephron mass
- PMID: 37800660
- PMCID: PMC10715706
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000932
Climate change and its influence in nephron mass
Abstract
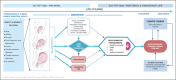
Purpose of review: The consequences of climate change, including heat and extreme weather events impact kidney function in adults and children. The impacts of climate change on kidney development during gestation and thereby on kidney function later in life have been poorly described. Clinical evidence is summarized to highlight possible associations between climate change and nephron mass.
Recent findings: Pregnant women are vulnerable to the effects of climate change, being less able to thermoregulate, more sensitive to the effects of dehydration, and more susceptible to infections. Exposure to heat, wildfire smoke, drought, floods and climate-related infections are associated with low birth weight, preterm birth and preeclampsia. These factors are associated with reduced nephron numbers, kidney dysfunction and higher blood pressures in offspring in later life. Exposure to air pollution is associated with higher blood pressures in children and has variable effects on estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Summary: Climate change has important impacts on pregnant women and their unborn children. Being born too small or too soon is associated with life-time risk of kidney disease. Climate change may therefore have a dual effect of impacting fetal kidney development and contributing to cumulative postnatal kidney injury. The impact on population kidney health of future generations may be significant.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antenatal and intrapartum interventions for preventing cerebral palsy: an overview of Cochrane systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 8;8(8):CD012077. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012077.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28786098 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin for women who are overweight or obese during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 24;7(7):CD010564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30039871 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and subsequent management for thyroid dysfunction pre-pregnancy and during pregnancy for improving maternal and infant health.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 21;2015(9):CD011263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26387772 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium supplementation commencing before or early in pregnancy, or food fortification with calcium, for preventing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 26;9(9):CD011192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011192.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 16;9:CD011192. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011192.pub3. PMID: 28949421 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sickle Cell Disease.2003 Sep 15 [updated 2025 Feb 13]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2003 Sep 15 [updated 2025 Feb 13]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301551 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of maternal health on neonatal and long-term kidney outcomes.Pediatr Nephrol. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s00467-025-06771-9. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40459611
References
-
- Levin A, Tonelli M, Bonventre J, et al. . Global kidney health 2017 and beyond: a roadmap for closing gaps in care, research, and policy. Lancet 2017; 390:1888–1917. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Varghese BM, Hansen A, et al. . Hot weather as a risk factor for kidney disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. Sci Total Environ 2021; 801:149806. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Trabanino R, Jarquin E, Wesseling C, et al. . Heat stress, dehydration, and kidney function in sugarcane cutters in El Salvador—a cross-shift study of workers at risk of Mesoamerican nephropathy. Environ Res 2015; 142:746–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

