In-depth biological characterization of two black soldier fly anti- Pseudomonas peptides reveals LPS-binding and immunomodulating effects
- PMID: 37800918
- PMCID: PMC10597467
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00454-23
In-depth biological characterization of two black soldier fly anti- Pseudomonas peptides reveals LPS-binding and immunomodulating effects
Abstract
As effector molecules of the innate immune system, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have gathered substantial interest as a potential future generation of antibiotics. Here, we demonstrate the anti-Pseudomonas activity and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding ability of HC1 and HC10, two cecropin peptides from the black soldier fly (Hermetia Illucens). Both peptides are active against a wide range of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains, including drug-resistant clinical isolates. Moreover, HC1 and HC10 can bind to lipid A, the toxic center of LPS and reduce the LPS-induced nitric oxide and cytokine production in murine macrophage cells. This suggests that the peptide-LPS binding can also lower the strong inflammatory response associated with P. aeruginosa infections. As the activity of AMPs is often influenced by the presence of salts, we studied the LPS-binding activity of HC1 and HC10 in physiological salt concentrations, revealing a strong decrease in activity. Our research confirmed the early potential of HC1 and HC10 as starting points for anti-Pseudomonas drugs, as well as the need for structural or formulation optimization before further preclinical development can be considered. IMPORTANCE The high mortality and morbidity associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections remain an ongoing challenge in clinical practice that requires urgent action. P. aeruginosa mostly infects immunocompromised individuals, and its prevalence is especially high in urgent care hospital settings. Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) are outer membrane structures that are responsible for inducing the innate immune cascade upon infection. P. aeruginosa LPS can cause local excessive inflammation, or spread systemically throughout the body, leading to multi-organ failure and septic shock. As antimicrobial resistance rates in P. aeruginosa infections are rising, the research and development of new antimicrobial agents remain indispensable. Especially, antimicrobials that can both kill the bacteria themselves and neutralize their toxins are of great interest in P. aeruginosa research to develop as the next generation of drugs.
Keywords: LPS binding; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antimicrobial peptides; black soldier fly; lipopolysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

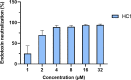

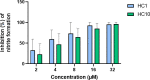

Similar articles
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0166421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01664-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985302 Free PMC article.
-
An attacin antimicrobial peptide, Hill_BB_C10074, from Hermetia illucens with anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa activity.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Dec 1;23(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-03131-1. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38036998 Free PMC article.
-
A novel family of defensin-like peptides from Hermetia illucens with antibacterial properties.BMC Microbiol. 2024 May 16;24(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03325-1. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38755524 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides from Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Potential Antimicrobial Factors Representing an Alternative to Antibiotics in Livestock Farming.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;11(7):1937. doi: 10.3390/ani11071937. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)-host defense antibacterial peptides interactions: role in bacterial resistance and prevention of sepsis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Sep;1758(9):1513-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.05.017. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16854372 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of a Mixture of Protein Hydrolysate from Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Schizochytrium on Palatability, Plasma Biochemistry, and Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Capacity in Cat Diets.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 28;14(5):751. doi: 10.3390/ani14050751. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473136 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Dietary Protein Hydrolysate from Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Schizochytrium on Palatability, Nutrient Metabolites and Health Status in Beagle Dogs.Metabolites. 2024 Mar 14;14(3):165. doi: 10.3390/metabo14030165. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38535325 Free PMC article.
-
Polymyxin B Peptide Hydrogel Coating: A Novel Approach to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 24;25(19):10269. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910269. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2017. WHO priority pathogens list for R&D of new antibiotics. Geneva:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

