Urine Proteomics Link Complement Activation with Interstitial Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy in Lupus Nephritis Patients
- PMID: 37802003
- PMCID: PMC10783434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152263
Urine Proteomics Link Complement Activation with Interstitial Fibrosis/Tubular Atrophy in Lupus Nephritis Patients
Abstract
Background: Intrarenal complement activation has been implicated in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in lupus nephritis (LN) based on prior animal studies. The assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC) by complement C5b to C9 on the cell membrane leads to cytotoxic pores and cell lysis, while CD59 inhibits MAC formation by preventing C9 from joining the complex. We hypothesize that complement activation and imbalance between complement activation and inhibition, as defined by increased production of individual complement components and uncontrolled MAC activation relative to CD59 inhibition, are associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in LN and correlate with the key mediators of kidney fibrosis- transforming growth factor receptors beta (TGFRβ), platelet-derived growth factor beta (PDGFβ) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRβ).
Methods: We included urine samples from 46 adults and pediatric biopsy-proven lupus nephritis patients who underwent clinically indicated kidney biopsies between 2010 and 2019. We compared individual urinary complement components and the urinary C9-to-CD59 ratio between LN patients with moderate/severe IFTA and none/mild IFTA. IFTA was defined as none/mild (<25% of interstitium affected) versus moderate/severe (≥ 25% of interstitium affected). Proteomics analysis was performed using mass spectrometry (Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, Thermo Scientific) and processed by the Proteome Discoverer. Urinary complement proteins enriched in LN patients with moderate/severe IFTA were correlated with serum creatinine, TGFβR1, TGFβR2, PDGFβ, and PDGFRβ.
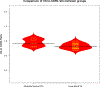
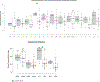
Results: Of the 46 LN patients included in the study, 41 (89.1%) were women, 20 (43.5%) self-identified as Hispanic or Latino, and 26 (56.5%) self-identified as Black or African American. Ten of the 46 (21.7%) LN patients had moderate/severe IFTA on kidney biopsy. LN patients with moderate/severe IFTA had an increased urinary C9-to-CD59 ratio [median 0.91 (0.83-1.05) vs 0.81 (0.76-0.91), p=0.01]. Urinary C3 and CFI levels in LN patients with moderate/severe IFTA were higher compared to those with none/mild IFTA [C3 median (IQR) 24.4(23.5-25.5) vs. 20.2 (18.5-22.2), p= 0.02], [CFI medium (IQR) 28.8 (21.8-30.6) vs. 20.4 (18.5-22.9), p=0.01]. Complement C9, CD59, C3 and CFI correlated with TGFβR1, PDGFβ, and PDGFRβ, while C9, CD59 and C3 correlated with TGFβR2.
Conclusion: This study is one of the first to compare the urinary complement profile in LN patients with moderate/severe IFTA and none/mild IFTA in human tissues. This study identified C3, CFI, and C9-to-CD59 ratio as potential markers of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in LN.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Complement; Kidney fibrosis; Lupus nephritis.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane attack complex (MAC) deposition in renal tubules is associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy: a pilot study.Lupus Sci Med. 2022 Jan;9(1):e000576. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2021-000576. Lupus Sci Med. 2022. PMID: 34996855 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with worsening interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy in lupus nephritis patients undergoing clinically indicated repeat kidney biopsy.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Apr 12;26(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04108-0. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40221666 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting kidney outcomes among Latin American patients with lupus nephritis: The prognostic value of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy and tubulointerstitial inflammation.Lupus. 2023 Mar;32(3):411-423. doi: 10.1177/09612033231151597. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Lupus. 2023. PMID: 36647707
-
Treatment of Rare Inflammatory Kidney Diseases: Drugs Targeting the Terminal Complement Pathway.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 10;11:599417. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.599417. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary biomarkers in childhood lupus nephritis.Clin Immunol. 2017 Dec;185:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27373868 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary Biomarkers for Lupus Nephritis: A Systems Biology Approach.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 18;13(8):2339. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082339. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α is a critical factor for the production of complement components in the liver.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Dec;60(10):1174-1183. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00972-6. Epub 2024 Sep 16. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 39285151
-
The past 25 years in paediatric rheumatology: insights from monogenic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024 Sep;20(9):585-593. doi: 10.1038/s41584-024-01145-1. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 39112602 Review.
-
Complement Activation in Nephrotic Glomerular Diseases.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 18;12(2):455. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020455. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary complement biomarkers in immune-mediated kidney diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1357869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1357869. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38895123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mok CC, Kwok RC, Yip PS. Effect of renal disease on the standardized mortality ratio and life expectancy of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2013;65(8):2154–60. - PubMed
-
- Furie R, Rovin BH, Houssiau F, Malvar A, Teng YKO, Contreras G, et al. Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. The New England journal of medicine. 2020;383(12):1117–28. - PubMed
-
- Rovin BH, Teng YKO, Ginzler EM, Arriens C, Caster DJ, Romero-Diaz J, et al. Efficacy and safety of voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): a double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397(10289):2070–80. - PubMed
-
- Ginzler EM, Dooley MA, Aranow C, Kim MY, Buyon J, Merrill JT, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;353(21):2219–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

