Human pallial MGE-type GABAergic interneuron cell therapy for chronic focal epilepsy
- PMID: 37802038
- PMCID: PMC10993865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.08.013
Human pallial MGE-type GABAergic interneuron cell therapy for chronic focal epilepsy
Abstract
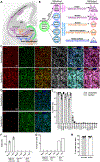
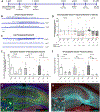
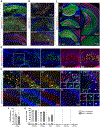
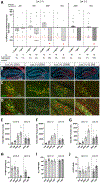
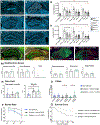
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE) is the most common focal epilepsy. One-third of patients have drug-refractory seizures and are left with suboptimal therapeutic options such as brain tissue-destructive surgery. Here, we report the development and characterization of a cell therapy alternative for drug-resistant MTLE, which is derived from a human embryonic stem cell line and comprises cryopreserved, post-mitotic, medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) pallial-type GABAergic interneurons. Single-dose intrahippocampal delivery of the interneurons in a mouse model of chronic MTLE resulted in consistent mesiotemporal seizure suppression, with most animals becoming seizure-free and surviving longer. The grafted interneurons dispersed locally, functionally integrated, persisted long term, and significantly reduced dentate granule cell dispersion, a pathological hallmark of MTLE. These disease-modifying effects were dose-dependent, with a broad therapeutic range. No adverse effects were observed. These findings support an ongoing phase 1/2 clinical trial (NCT05135091) for drug-resistant MTLE.
Keywords: GABA; MGE; TLE; cell therapy; epilepsy; hESC; interneuron; seizure; transplant.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests All authors except for L.Z. are employees and/or shareholders of Neurona Therapeutics Inc. C.R.N., J.R., A.K., and A.A.-B. are founders of Neurona. J.R., A.K., and A.A.-B. are members of the scientific advisory board at Neurona.
Figures


References
-
- Fisher RS, van Emde Boas W, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, and Engel J Jr. (2005). Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46, 470–472. - PubMed
-
- Leppik IE (1992). Intractable epilepsy in adults. Epilepsy Res. Suppl 5, 7–11. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt D, and Löscher W (2005). Drug resistance in epilepsy: putative neurobiologic and clinical mechanisms. Epilepsia 46, 858–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

