Deconstructing the integrated oscillator model for pancreatic β-cells
- PMID: 37802364
- PMCID: PMC10991200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2023.109085
Deconstructing the integrated oscillator model for pancreatic β-cells
Abstract
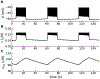
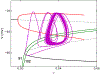
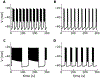
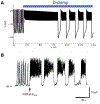
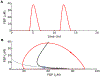
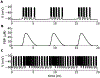
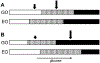
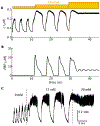
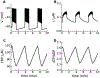
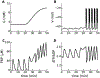
Electrical bursting oscillations in the β-cells of pancreatic islets have been a focus of investigation for more than fifty years. This has been aided by mathematical models, which are descendants of the pioneering Chay-Keizer model. This article describes the key biophysical and mathematical elements of this model, and then describes the path forward from there to the Integrated Oscillator Model (IOM). It is both a history and a deconstruction of the IOM that describes the various elements that have been added to the model over time, and the motivation for adding them. Finally, the article is a celebration of the 40th anniversary of the publication of the Chay-Keizer model.
Keywords: Beta-cells; Electrical bursting; Fast/slow analysis; Islets.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures
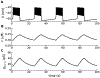
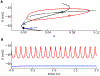
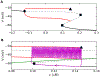
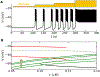


References
-
- Antunes CM, Salgado AP, Rosário LM, and Santos RM, Differential patterns of glucose-induced electrical activity and intracellular calcium responses in single mouse and rat pancreatic islets, Diabetes, 49 (2000), pp. 2028–2038. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, and Ashcroft SJH, Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic β-cells, Nature, 312 (1984), pp. 446–448. - PubMed
-
- Atwater I, Dawson CM, Scott A, Eddlestone G, and Rojas E, The nature of the oscillatory behavior in electrical activity for pancreatic β-cell, in Biochemistry and Biophysics of the Pancreatic β-cell, Thieme G, ed., Verlag, New York, 1980, pp. 100–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

