Rhodococcus erythropolis septic arthritis
- PMID: 37802590
- PMCID: PMC10565188
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2023-256864
Rhodococcus erythropolis septic arthritis
Abstract
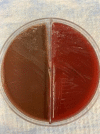
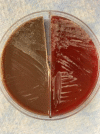
A woman in her 50s presented with a 4-day history of left knee pain, erythema, swelling as well as malaise and rigours 1 month after undergoing a left knee meniscectomy. She was diagnosed with left native knee septic arthritis and underwent arthroscopic irrigation and debridement of the knee; cultures from synovial tissue grew Rhodococcus erythropolis. Rhodococcus spp are soil-dwelling and livestock-dwelling bacteria which occasionally cause disease in immunocompromised hosts. Infection in immunocompetent hosts is rare, and septic arthritis secondary to Rhodococcus erythropolis has not been reported previously.
Keywords: Bone and joint infections; Orthopaedics.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous