Bladder cancer intrinsic LRFN2 drives anticancer immunotherapy resistance by attenuating CD8+ T cell infiltration and functional transition
- PMID: 37802603
- PMCID: PMC10565151
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007230
Bladder cancer intrinsic LRFN2 drives anticancer immunotherapy resistance by attenuating CD8+ T cell infiltration and functional transition
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy improves the survival of patients with advanced bladder cancer (BLCA); however, its overall effectiveness is limited, and many patients still develop immunotherapy resistance. The leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type-III domain-containing protein (LRFN) family has previously been implicated in regulating brain dysfunction; however, the mechanisms underlying the effect of LRFN2 on the tumor microenvironment (TME) and immunotherapy remain unclear.
Methods: Here we combined bulk RNA sequencing, single-cell RNA sequencing, ProcartaPlex multiple immunoassays, functional experiments, and TissueFAXS panoramic tissue quantification assays to demonstrate that LRFN2 shapes a non-inflammatory TME in BLCA.
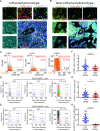
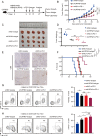
Results: First, comprehensive multiomics analysis identified LRFN2 as a novel immunosuppressive target specific to BLCA. We found that tumor-intrinsic LRFN2 inhibited the recruitment and functional transition of CD8+ T cells by reducing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and this mechanism was verified in vitro and in vivo. LRFN2 restrained antitumor immunity by inhibiting the infiltration, proliferation, and differentiation of CD8+ T cells in vitro. Furthermore, a spatial exclusivity relationship was observed between LRFN2+ tumor cells and CD8+ T cells and cell markers programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and T cell factor 1 (TCF-1). Preclinically, LRFN2 knockdown significantly enhanced the efficacy of ICI therapy. Clinically, LRFN2 can predict immunotherapy responses in real-world and public immunotherapy cohorts. Our results reveal a new role for LRFN2 in tumor immune evasion by regulating chemokine secretion and inhibiting CD8+ T-cell recruitment and functional transition.
Conclusions: Thus, LRFN2 represents a new target that can be combined with ICIs to provide a potential treatment option for BLCA.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Tumor Microenvironment; Urinary Bladder Neoplasms.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
