MetaCC allows scalable and integrative analyses of both long-read and short-read metagenomic Hi-C data
- PMID: 37802989
- PMCID: PMC10558524
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41209-6
MetaCC allows scalable and integrative analyses of both long-read and short-read metagenomic Hi-C data
Abstract
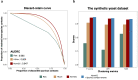
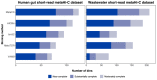
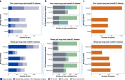
Metagenomic Hi-C (metaHi-C) can identify contig-to-contig relationships with respect to their proximity within the same physical cell. Shotgun libraries in metaHi-C experiments can be constructed by next-generation sequencing (short-read metaHi-C) or more recent third-generation sequencing (long-read metaHi-C). However, all existing metaHi-C analysis methods are developed and benchmarked on short-read metaHi-C datasets and there exists much room for improvement in terms of more scalable and stable analyses, especially for long-read metaHi-C data. Here we report MetaCC, an efficient and integrative framework for analyzing both short-read and long-read metaHi-C datasets. MetaCC outperforms existing methods on normalization and binning. In particular, the MetaCC normalization module, named NormCC, is more than 3000 times faster than the current state-of-the-art method HiCzin on a complex wastewater dataset. When applied to one sheep gut long-read metaHi-C dataset, MetaCC binning module can retrieve 709 high-quality genomes with the largest species diversity using one single sample, including an expansion of five uncultured members from the order Erysipelotrichales, and is the only binner that can recover the genome of one important species Bacteroides vulgatus. Further plasmid analyses reveal that MetaCC binning is able to capture multi-copy plasmids.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

