A circulating cell-free DNA methylation signature for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37803338
- PMCID: PMC10557228
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01872-1
A circulating cell-free DNA methylation signature for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
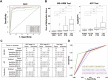
To address the shortcomings of current hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance tests, we set out to find HCC-specific methylation markers and develop a highly sensitive polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method to detect them in circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA). The analysis of large methylome data revealed that Ring Finger Protein 135 (RNF135) and Lactate Dehydrogenase B (LDHB) are universally applicable HCC methylation markers with no discernible methylation level detected in any other tissue types. These markers were used to develop Methylation Sensitive High-Resolution Analysis (MS-HRM), and their diagnostic accuracy was tested using cfDNA from healthy, at-risk, and HCC patients. The combined MS-HRM RNF135 and LDHB analysis detected 57% of HCC, outperforming the alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test's sensitivity of 45% at comparable specificity. Furthermore, when used with the AFP test, the methylation assay can detect 70% of HCC. Our findings suggest that the cfDNA methylation assay could be used for HCC liquid biopsy.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer diagnosis; Cell-free DNA; DNA methylation.; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liquid biopsy; Methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

