The Effect of Calcium hydroxide, Glass Ionomer and light cured resin modified calcium silicate on viability, proliferation and differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
- PMID: 37803363
- PMCID: PMC10557230
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03429-6
The Effect of Calcium hydroxide, Glass Ionomer and light cured resin modified calcium silicate on viability, proliferation and differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
Abstract
Background: Vital pulp therapy, based on the use of stem cells, has promising research and therapeutic applications in dentistry. It is essential to understand the direct effect of capping materials on the dental pulp stem cells of primary teeth, which contribute to the healing powers of the tooth. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of different capping materials (Calcium Hydroxide (DyCal®) - Glass Ionomer (Fuji IX®) and light-cured resin modified calcium silicate (TheraCal LC®)) on the viability, proliferation, and differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs).
Methods: SHEDs were isolated from extracted primary teeth, then divided into four groups and each of the capping materials were applied to the stem cells as follows: group I the controls, group II with Ca(OH)2, group III with the GIC, and group IV with the Theracal LC. For all groups assessment of viability and proliferation rate was done using the MTT cell proliferation assay. Also, Differentiation was evaluated by measuring the gene expression of Alkaline phosphatase enzyme activity (ALP) and Dentin matrix protein-1 (DMP1) through quantitative real-time PCR. Morphological assessment was conducted using Alizarin Red S staining. All evaluations were performed after 7 and 14 days of culture.
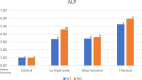
Results: TheraCal LC showed the highest values of proliferation, which was significant only compared to the control group after 2 weeks (p = 0.012). After one week, TheraCal LC showed the highest significant values of ALP and DMP1 compared to all other groups (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The three materials under study are biocompatible, maintain viability, and stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of SHEDs. However, TheraCal LC allows better proliferation of SHEDs than Dycal Ca(OH)2 and Fuji IX GIC.
Keywords: Calcium hydroxide; Differentiation; Glass ionomer cement; Primary teeth; Proliferation; SHEDs; TheraCal LC; Vital pulp therapy.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Primate pulpal healing after exposure and TheraCal application.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2014 Summer;38(4):333-7. doi: 10.17796/jcpd.38.4.m585322121536q71. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2014. PMID: 25571685
-
Comparative Evaluation of Effectiveness of Calcium Hydroxide, MTA, and TheraCal LC in Indirect Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: In Vivo Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024 Apr 1;25(4):365-371. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3680. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024. PMID: 38956853 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate, BiodentineTM and calcium hydroxide on viability, proliferation, migration and differentiation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.J Appl Oral Sci. 2018 Feb 1;26:e20160629. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2016-0629. J Appl Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 29412365 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Inductive Materials in Direct and Indirect Pulp Capping-A Review Article.Materials (Basel). 2020 Mar 7;13(5):1204. doi: 10.3390/ma13051204. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32155997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TheraCal LC: From Biochemical and Bioactive Properties to Clinical Applications.Int J Dent. 2018 Mar 26;2018:3484653. doi: 10.1155/2018/3484653. eCollection 2018. Int J Dent. 2018. PMID: 29785184 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the biocompatibility of various pulp capping materials on zebrafish model.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 20;19(9):e0310996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310996. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39302990 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity and proliferation effects of cold ceramic on stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth compared to MTA: an in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 13;25(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05756-2. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40082877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sultan N, Amin LE, Zaher AR, Scheven BA, Grawish ME. Dental pulp stem cells: Novel cell-based and cell-free therapy for peripheral nerve repair. World J Stomatol. 2019;7(1):1–19. doi: 10.5321/wjs.v7.i1.1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

