Anoikis resistance and immune escape mediated by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1-induced stabilization of PGC-1α promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 37803433
- PMCID: PMC10559433
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02835-6
Anoikis resistance and immune escape mediated by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1-induced stabilization of PGC-1α promotes invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the first discovered human tumor virus that is associated with a variety of malignancies of both lymphoid and epithelial origin including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). The EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) has been well-defined as a potent oncogenic protein, which is intimately correlated with NPC pathogenesis. Anoikis is considered to be a physiological barrier to metastasis, and avoiding anoikis is a major hallmark of metastasis. However, the role of LMP1 in anoikis-resistance and metastasis of NPC has not been fully identified.
Methods: Trypan blue staining, colony formation assay, flow cytometry, and TUNEL staining, as well as the detection of apoptosis and anoikis resistance-related markers was applied to evaluate the anoikis-resistant capability of NPC cells cultured in ultra-low adhesion condition. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiment was performed to determine the interaction among LMP1, PRMT1 and PGC-1α. Ex vivo ubiquitination assay was used to detect the ubiquitination level of PGC-1α. Anoikis- resistant LMP1-positive NPC cell lines were established and applied for the xenograft and metastatic animal experiments.
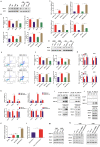
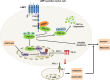
Results: Our current findings reveal the role of LMP1-stabilized peroxisome proliferator activated receptor coactivator-1a (PGC-1α) in anoikis resistance and immune escape to support the invasion and metastasis of NPC. Mechanistically, LMP1 enhances PGC-1α protein stability by promoting the interaction between arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) and PGC-1α to elevate the methylation modification of PGC-1α, thus endowing NPC cells with anoikis-resistance. Meanwhile, PGC-1α mediates the immune escape induced by LMP1 by coactivating with STAT3 to transcriptionally up-regulate PD-L1 expression.
Conclusion: Our work provides insights into how virus-encoded proteins recruit and interact with host regulatory elements to facilitate the malignant progression of NPC. Therefore, targeting PGC-1α or PRMT1-PGC-1α interaction might be exploited for therapeutic gain for EBV-associated malignancies.
Keywords: Anoikis resistance; Immune escape; LMP1; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; PGC-1α.
© 2023. Italian National Cancer Institute ‘Regina Elena’.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

