BARN: Behavior-Aware Relation Network for multi-label behavior detection in socially housed macaques
- PMID: 37804114
- PMCID: PMC10802107
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.485
BARN: Behavior-Aware Relation Network for multi-label behavior detection in socially housed macaques
Abstract
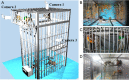
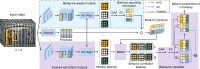
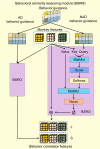
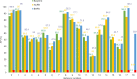
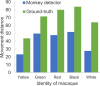
Quantification of behaviors in macaques provides crucial support for various scientific disciplines, including pharmacology, neuroscience, and ethology. Despite recent advancements in the analysis of macaque behavior, research on multi-label behavior detection in socially housed macaques, including consideration of interactions among them, remains scarce. Given the lack of relevant approaches and datasets, we developed the Behavior-Aware Relation Network (BARN) for multi-label behavior detection of socially housed macaques. Our approach models the relationship of behavioral similarity between macaques, guided by a behavior-aware module and novel behavior classifier, which is suitable for multi-label classification. We also constructed a behavior dataset of rhesus macaques using ordinary RGB cameras mounted outside their cages. The dataset included 65 913 labels for 19 behaviors and 60 367 proposals, including identities and locations of the macaques. Experimental results showed that BARN significantly improved the baseline SlowFast network and outperformed existing relation networks. In conclusion, we successfully achieved multi-label behavior detection of socially housed macaques with both economic efficiency and high accuracy.
猕猴行为的量化在许多领域的研究中提供了关键的实验支持,如药物安全评估、神经科学和动物行为学。近些年来,许多研究人员致力于猕猴的行为分析。然而,很少有工作研究群居猕猴的多标签行为检测。该任务考虑了猕猴之间的交互,更符合群居猕猴的特征。鉴于缺乏和该任务相关的方法和数据集,在该文中我们提出了一个用于群居猕猴多标签行为检测的行为感知关系网络(BARN)。该网络在一个行为感知模块的指导下建模了猕猴之间的行为相似性这一关系,还包含一个新颖的更适用于多标签分类的行为分类器。我们还利用安装在笼子外的普通RGB相机构建了一个恒河猴的行为数据集。数据注释包含65 913个对应于19种行为的标签和60 367个包括猕猴的身份和位置的提议(proposals)。实验结果表明BARN对基线网络SlowFast取得了显著改进并且由于现有的关系网络。总的来说,我们以低成本和高精度成功地完成了群居猕猴的多标签行为检测。.
Keywords: Behavioral similarity; Drug safety assessment; Macaque behavior; Multi-label behavior detection; Relation network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[A multi-behavior recognition method for macaques based on improved SlowFast network].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Apr 25;40(2):257-264. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202112014. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37139756 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Social management of laboratory rhesus macaques housed in large groups using a network approach: A review.Behav Processes. 2018 Nov;156:77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2017.11.014. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Behav Processes. 2018. PMID: 29224844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MacqD deep-learning-based model for automatic detection of socially housed laboratory macaques.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95180-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195447 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of outdoor housing on self-injurious and stereotypic behavior in adult male rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2006 Sep;45(5):35-43. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2006. PMID: 16995645
-
Laboratory rhesus macaque social housing and social changes: Implications for research.Am J Primatol. 2017 Jan;79(1):1-14. doi: 10.1002/ajp.22528. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Am J Primatol. 2017. PMID: 26848542 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
InteBOMB: Integrating generic object tracking and segmentation with pose estimation for animal behavior analysis.Zool Res. 2025 Mar 18;46(2):355-369. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.268. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 40049663 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Collobert R, Bengio S, Mariéthoz J. 2002. Torch: a modular machine learning software library. REP_WORK (30 October, 2002). Idiap, https://os.unil.cloud.switch.ch/tind-customer-epfl/5ea06583-58ae-4f33-bcc5-ae8feb746af1?response-content-disposition=attachment%3B%20filename%2A%3DUTF-8%27%27rr02-46.pdf&response-content-type=application%2Fpdf&AWSAccessKeyId=ded3589a13b4450889b2f728d54861a6&Expires=1682421084&Signature=gej7yCqVtYuJiwgttsO0YPoiqXo%3D.
-
-
-
Defler TR. 2000. Locomotion and posture in Lagothrix lagotricha. Folia Primatologica, 70(6): 313–327.
-
-
- Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams CKI, et al The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International journal of computer vision. 2010;88(2):303–338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
