Drosophila CASK regulates brain size and neuronal morphogenesis, providing a genetic model of postnatal microcephaly suitable for drug discovery
- PMID: 37805506
- PMCID: PMC10559581
- DOI: 10.1186/s13064-023-00174-y
Drosophila CASK regulates brain size and neuronal morphogenesis, providing a genetic model of postnatal microcephaly suitable for drug discovery
Abstract
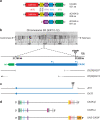
Background: CASK-related neurodevelopmental disorders are untreatable. Affected children show variable severity, with microcephaly, intellectual disability (ID), and short stature as common features. X-linked human CASK shows dosage sensitivity with haploinsufficiency in females. CASK protein has multiple domains, binding partners, and proposed functions at synapses and in the nucleus. Human and Drosophila CASK show high amino-acid-sequence similarity in all functional domains. Flies homozygous for a hypomorphic CASK mutation (∆18) have motor and cognitive deficits. A Drosophila genetic model of CASK-related disorders could have great scientific and translational value.
Methods: We assessed the effects of CASK loss of function on morphological phenotypes in Drosophila using established genetic, histological, and primary neuronal culture approaches. NeuronMetrics software was used to quantify neurite-arbor morphology. Standard nonparametric statistics methods were supplemented by linear mixed effects modeling in some cases. Microfluidic devices of varied dimensions were fabricated and numerous fluid-flow parameters were used to induce oscillatory stress fields on CNS tissue. Dissociation into viable neurons and neurite outgrowth in vitro were assessed.
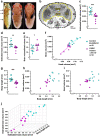
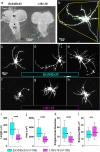
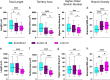
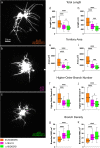
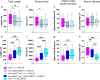
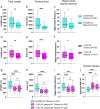
Results: We demonstrated that ∆18 homozygous flies have small brains, small heads, and short bodies. When neurons from developing CASK-mutant CNS were cultured in vitro, they grew small neurite arbors with a distinctive, quantifiable "bushy" morphology that was significantly rescued by transgenic CASK+. As in humans, the bushy phenotype showed dosage-sensitive severity. To overcome the limitations of manual tissue trituration for neuronal culture, we optimized the design and operation of a microfluidic system for standardized, automated dissociation of CNS tissue into individual viable neurons. Neurons from CASK-mutant CNS dissociated in the microfluidic system recapitulate the bushy morphology. Moreover, for any given genotype, device-dissociated neurons grew larger arbors than did manually dissociated neurons. This automated dissociation method is also effective for rodent CNS.
Conclusions: These biological and engineering advances set the stage for drug discovery using the Drosophila model of CASK-related disorders. The bushy phenotype provides a cell-based assay for compound screening. Nearly a dozen genes encoding CASK-binding proteins or transcriptional targets also have brain-development mutant phenotypes, including ID. Hence, drugs that improve CASK phenotypes might also benefit children with disorders due to mutant CASK partners.
Keywords: Haploinsufficiency; Immunostaining; Intellectual disability; Microfluidics; Neurite arbor; Neurogenetics; Primary neuronal culture; Short stature.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two microcephaly-associated novel missense mutations in CASK specifically disrupt the CASK-neurexin interaction.Hum Genet. 2018 Mar;137(3):231-246. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1874-3. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29426960 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and molecular insights into CASK-related disorders in males.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Apr 12;10:44. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0256-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 25886057 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive investigation of CASK mutations and other genetic etiologies in 41 patients with intellectual disability and microcephaly with pontine and cerebellar hypoplasia (MICPCH).PLoS One. 2017 Aug 7;12(8):e0181791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181791. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28783747 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Clinical Phenotypes of CASK-Related Disorders and Multiple Functional Domains of CASK Protein.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 20;14(8):1656. doi: 10.3390/genes14081656. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Non-Linear Path from Gene Dysfunction to Genetic Disease: Lessons from the MICPCH Mouse Model.Cells. 2022 Mar 28;11(7):1131. doi: 10.3390/cells11071131. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anonymous, editors. Geneticist seeks engineer: must like flies and worms. Nat Methods. 2007;4(6):463. https://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth0607-463. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ali H, Blackmore M, Bixby JL, Lemmon VP. High content screening with primary neurons. 2013 [updated 2014 Oct 1]. In: Markossian S, Grossman A, Brimacombe K, et al., editors. Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. NCBI Bookshelf ID: NBK169433. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK169433/. Accessed 20 Aug 2023.
-
- Al-Mofty S, Elsayed M, Ali H, Ahmed O, Altayyeb A, Wahby A, et al. A microfluidic platform for dissociating clinical scale tissue samples into single cells. Biomed Microdevices. 2021;23:10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

