Upregulation of exosome secretion from tumor-associated macrophages plays a key role in the suppression of anti-tumor immunity
- PMID: 37805922
- PMCID: PMC10697782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113224
Upregulation of exosome secretion from tumor-associated macrophages plays a key role in the suppression of anti-tumor immunity
Abstract
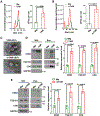
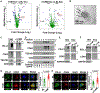
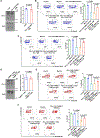
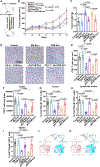
Macrophages play a pivotal role in tumor immunity. We report that reprogramming of macrophages to tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) promotes the secretion of exosomes. Mechanistically, increased exosome secretion is driven by MADD, which is phosphorylated by Akt upon TAM induction and activates Rab27a. TAM exosomes carry high levels of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and potently suppress the proliferation and function of CD8+ T cells. Analysis of patient melanoma tissues indicates that TAM exosomes contribute significantly to CD8+ T cell suppression. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis showed that exosome-related genes are highly expressed in macrophages in melanoma; TAM-specific RAB27A expression inversely correlates with CD8+ T cell infiltration. In a murine melanoma model, lipid nanoparticle delivery of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting macrophage RAB27A led to better T cell activation and sensitized tumors to anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) treatment. Our study demonstrates tumors use TAM exosomes to combat CD8 T cells and suggests targeting TAM exosomes as a potential strategy to improve immunotherapies.
Keywords: CP: Cancer; CP: Immunology; exosome; immunotherapy; programmed cell death ligand 1; tumor-associated macrophages.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

