Sensory spinal interoceptive pathways and energy balance regulation
- PMID: 37806487
- PMCID: PMC10590858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101817
Sensory spinal interoceptive pathways and energy balance regulation
Abstract
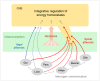
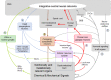
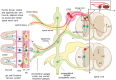
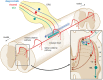
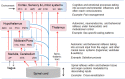
Interoception plays an important role in homeostatic regulation of energy intake and metabolism. Major interoceptive pathways include gut-to-brain and adipose tissue-to brain signaling via vagal sensory nerves and hormones, such as leptin. However, signaling via spinal sensory neurons is rapidly emerging as an additional important signaling pathway. Here we provide an in-depth review of the known anatomy and functions of spinal sensory pathways and discuss potential mechanisms relevant for energy balance homeostasis in health and disease. Because sensory innervation by dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons goes far beyond vagally innervated viscera and includes adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and skin, it is in a position to provide much more complete metabolic information to the brain. Molecular and anatomical identification of function specific DRG neurons will be important steps in designing pharmacological and neuromodulation approaches to affect energy balance regulation in disease states such as obesity, diabetes, and cancer.
Keywords: Diabetes; Energy expenditure; Food intake; Gut-brain communication; Interoception; Interorgan communication; Obesity; Sensory nerves; Spinal cord.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Heike Muenzberg reports financial support was provided by National Institute of Health. Hans-Rudolf Berthoud reports financial support was provided by National Institute of Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interactions of Eosinophils with Nerves.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2241:161-181. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1095-4_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33486736
-
Spinal sensory innervation of the intestine.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;90:102973. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2025.102973. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39892315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of somatosensory innervation of adipose tissues.Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7927):569-574. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05137-7. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36045288 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory neurons expressing calcitonin gene-related peptide α regulate adaptive thermogenesis and diet-induced obesity.Mol Metab. 2021 Mar;45:101161. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101161. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33412345 Free PMC article.
-
[Sensory neural innervation of adipose tissue in metabolic disorders].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Oct 25;76(5):841-848. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39468820 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Gut-brain communication: Functional anatomy of vagal afferents.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;93:103058. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2025.103058. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40451136 Review.
-
Symptoms Arising From the Diaphragm Muscle: Function and Dysfunction.Cureus. 2024 Jan 29;16(1):e53143. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53143. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38288323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History and future of leptin: Discovery, regulation and signaling.Metabolism. 2024 Dec;161:156026. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.156026. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Metabolism. 2024. PMID: 39245434 Review.
-
Novel neural pathways targeted by GLP-1R agonists and bariatric surgery.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Feb;477(2):171-185. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03047-3. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 39644359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic interoception in health and disease.Auton Neurosci. 2024 Jun;253:103174. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2024.103174. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Auton Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38579493 Free PMC article. Review.
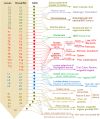
References
-
- Bray G.A., Kim K.K., Wilding J.P.H., World Obesity F. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev. 2017;18:715–723. - PubMed
-
- Qasim A., Turcotte M., de Souza R.J., Samaan M.C., Champredon D., Dushoff J., et al. On the origin of obesity: identifying the biological, environmental and cultural drivers of genetic risk among human populations. Obes Rev. 2018;19:121–149. - PubMed
-
- Dulloo A.G. Physiology of weight regain: lessons from the classic Minnesota Starvation Experiment on human body composition regulation. Obes Rev. 2021;22(Suppl 2) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

