Vilazodone, a Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor with Diminished Impact on Methylphenidate-Induced Gene Regulation in the Striatum: Role of 5-HT1A Receptor
- PMID: 37807008
- PMCID: PMC10978284
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-023-03688-y
Vilazodone, a Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor with Diminished Impact on Methylphenidate-Induced Gene Regulation in the Striatum: Role of 5-HT1A Receptor
Abstract
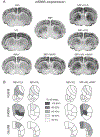
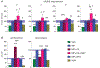
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including fluoxetine, are frequently combined with medical psychostimulants such as methylphenidate (Ritalin), for example, in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder/depression comorbidity. Co-exposure to these medications also occurs with misuse of methylphenidate as a recreational drug by patients on SSRIs. Methylphenidate, a dopamine reuptake blocker, produces moderate addiction-related gene regulation. Findings show that SSRIs such as fluoxetine given in conjunction with methylphenidate potentiate methylphenidate-induced gene regulation in the striatum in rats, consistent with a facilitatory action of serotonin on addiction-related processes. These SSRIs may thus increase methylphenidate's addiction liability. Here, we investigated the effects of a novel SSRI, vilazodone, on methylphenidate-induced gene regulation. Vilazodone differs from prototypical SSRIs in that, in addition to blocking serotonin reuptake, it acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor subtype. Studies showed that stimulation of the 5-HT1A receptor tempers serotonin input to the striatum. We compared the effects of acute treatment with vilazodone (10-20 mg/kg) with those of fluoxetine (5 mg/kg) on striatal gene regulation (zif268, substance P, enkephalin) induced by methylphenidate (5 mg/kg), by in situ hybridization histochemistry combined with autoradiography. We also assessed the impact of blocking 5-HT1A receptors by the selective antagonist WAY-100635 (0.5 mg/kg) on these responses. Behavioral effects of these drug treatments were examined in parallel in an open-field test. Our results show that, in contrast to fluoxetine, vilazodone did not potentiate gene regulation induced by methylphenidate in the striatum, while vilazodone enhanced methylphenidate-induced locomotor activity. However, blocking 5-HT1A receptors by WAY-100635 unmasked a potentiating effect of vilazodone on methylphenidate-induced gene regulation, thus confirming an inhibitory role for 5-HT1A receptors. Our findings suggest that vilazodone may serve as an adjunct SSRI with diminished addiction facilitating properties and identify the 5-HT1A receptor as a potential therapeutic target to treat addiction.
Keywords: Fluoxetine; Gene expression; Methylphenidate; Psychostimulant; SSRI; Striatum; Vilazodone; zif268.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vilazodone, a Novel SSRI Antidepressant with 5-HT1A Partial Agonist Properties: Diminished Potentiation of Chronic Oral Methylphenidate-Induced Dynorphin Expression in the Striatum in Adolescent Male Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4520-4532. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04569-8. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39466575 Free PMC article.
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants potentiate methylphenidate (Ritalin)-induced gene regulation in the adolescent striatum.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Aug;32(3):435-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07294.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20704593 Free PMC article.
-
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors potentiate gene blunting induced by repeated methylphenidate treatment: Zif268 versus Homer1a.Addict Biol. 2014 Nov;19(6):986-95. doi: 10.1111/adb.12067. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Addict Biol. 2014. PMID: 23763573 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin-dopamine interactions in psychostimulant-induced gene regulation: SSRI antidepressants potentiate gene regulation by methylphenidate (Ritalin) in the striatum and enhance behavioral profile indicative of addiction liability in rodents.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025 Aug 18;177:106344. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106344. Online ahead of print. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025. PMID: 40835201 Review.
-
Vilazodone: a 5-HT1A receptor agonist/serotonin transporter inhibitor for the treatment of affective disorders.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2009 Summer;15(2):107-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00067.x. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2009. PMID: 19499624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Chronic Oral Methylphenidate and Fluoxetine Decreases D2R Levels in the Caudate Putamen and Nucleus Accumbens.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jul 11;50(4):230. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04481-0. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40643764 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine potentiates methylphenidate-induced behavioral responses: Enhanced locomotion or stereotypies and facilitated acquisition of cocaine self-administration.Addict Neurosci. 2023 Dec 15;9:100131. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2023.100131. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Addict Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38222942 Free PMC article.
-
Vilazodone, a Novel SSRI Antidepressant with 5-HT1A Partial Agonist Properties: Diminished Potentiation of Chronic Oral Methylphenidate-Induced Dynorphin Expression in the Striatum in Adolescent Male Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4520-4532. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04569-8. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39466575 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring adverse events of Vilazodone: evidence from the FAERS database.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 May 16;24(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05813-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38755677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castle L, Aubert RE, Verbrugge RR, Khalid M, Epstein RS (2007) Trends in medication treatment for ADHD. J Atten Disord 10:335–342 - PubMed
-
- Kollins SH (2008) ADHD, substance use disorders, and psychostimulant treatment: current literature and treatment guidelines. J Atten Disord 12:115–125 - PubMed
-
- DSMMD, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition. 2000, Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

