Ivabradine in patients with heart failure: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 37808119
- PMCID: PMC10552613
- DOI: 10.1080/20016689.2023.2262073
Ivabradine in patients with heart failure: a systematic literature review
Abstract
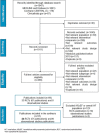
Background: Heart failure is a chronic disease linked with significant morbidity and mortality, and uncontrolled resting heart rate is a risk factor for adverse outcomes. This systematic literature review aimed to assess the efficacy, safety, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) of ivabradine in patients with heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies. Methods: We searched electronic databases from their inception to July 2021 to include studies that reported on efficacy, safety, or PROs of ivabradine in patients with HFrEF. Results: Of 1947 records screened, 51 RCTs and 6 observational studies were identified. Ivabradine on top of background therapy demonstrated a significant reduction in composite outcomes including hospitalization for HF or cardiovascular death. In addition, observational studies suggested that ivabradine was associated with a significant reduction in mortality. Across all studies, ivabradine use on top of background therapy was associated with greater reductions in heart rate, improved EF, and improved health-related quality of life (QoL) and comparable risk of total adverse events compared to those treated with background therapy alone. Conclusions: Ivabradine on top of background therapy is beneficial for heart rate, hospitalization risk for HF, mortality, EF, and patients' QoL. Moreover, these benefits were achieved with no significant increase in the overall risk of total adverse events.
Keywords: Heart failure; ivabradine; patient-reported outcomes; quality of life; systematic review.
© 2023 Putnam PHMR. Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have a conflict of interest. Briere Jean Baptiste is an employee of Servier, and Zeba M. Khan was a paid consultant for Servier International at the time of the study. Elzbieta Olewinska, Fatma Khrouf, and Mateusz Nikodem are employees of Putnam PHMR, which received funding from Servier to conduct the study. However, this funding did not influence the design, conduct, or reporting of the research presented in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of ivabradine on the cardiac function of chronic heart failure reduced ejection fraction: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Cardiol. 2021 Apr;44(4):463-471. doi: 10.1002/clc.23581. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Clin Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33638556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial effects of ivabradine in patients with heart failure, low ejection fraction, and heart rate above 77 b.p.m.ESC Heart Fail. 2019 Dec;6(6):1199-1207. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12513. Epub 2019 Oct 8. ESC Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 31591826 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Ivabradine on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function, Exercise Tolerance and Quality of Life in Patients With Heart Failure: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cardiol Res. 2020 Feb;11(1):40-49. doi: 10.14740/cr958. Epub 2020 Jan 26. Cardiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32095195 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials Assessing Clinical and Haemodynamic Outcomes of Ivabradine in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction Patients.Heart Lung Circ. 2024 Jul;33(7):962-974. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2023.09.005. Epub 2024 May 10. Heart Lung Circ. 2024. PMID: 38729854
-
Efficacy of ivabradine for heart failure: A protocol for a systematic review of randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(14):e15075. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015075. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30946357 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Herbal Interactions with Cardiac Medications: A Comprehensive Review of Potential Interactions between Herbal Drugs and Commonly Prescribed Cardiac Medications.Curr Drug Saf. 2025;20(2):94-119. doi: 10.2174/0115748863289321240424063819. Curr Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 38726779 Review.
-
Hardly a Windfall: Prescribing Practices in Pediatric Heart Failure Around Food and Drug Administration Approval.JACC Adv. 2025 Apr;4(4):101661. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101661. Epub 2025 Mar 19. JACC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40112573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the heart failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(27):2129–2200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous