Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- PMID: 37808167
- PMCID: PMC10552914
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2023-0812
Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
Abstract
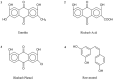
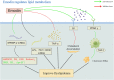
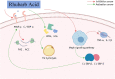
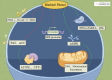
Hyperlipidemia is a metabolic disorder, which is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis, stroke, and coronary heart disease. Although lipid-lowering treatments have been extensively studied, safer treatments with fewer adverse effects are needed. Rhubarb is a traditional Chinese medicine that has lipid-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Disturbance in lipid metabolism is the basis of tissue damage caused by hyperlipidemia and plays a key role in the development of hyperlipidemia; however, the molecular mechanisms by which rhubarb regulates lipid metabolism to lower lipid levels are yet to be elucidated. We conducted this study to summarize the phytochemical constituents of Rheum officinale and provide a comprehensive review of the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of lipid metabolism during hyperlipidemia treatment. It was found that rhubarb extracts, including emodin, rhubarb acid, and rhubarb phenol, regulate total cholesterol, triglyceride, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels through signaling pathways such as C/EBP α, 3T3-L1, PPAR α, and AMPK, thereby improving the hyperlipidemic state. This suggests that rhubarb is a natural drug with lipid-lowering potential, and an in-depth exploration of its lipid-lowering mechanism can provide new ideas for the prevention and treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine; hyperlipidemia; lipid lowering; lipid metabolism; mechanism; rhubarb.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Wang L, Fan W, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Li L, Wang J, et al. Antiobesity, regulation of lipid metabolism, and attenuation of liver oxidative stress effects of hydroxy-α-sanshool isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum on high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5852494. 10.1155/2019/5852494. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
