Evaluation of anti-cancer effects of carnosine and melittin-loaded niosomes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- PMID: 37808196
- PMCID: PMC10552532
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1258387
Evaluation of anti-cancer effects of carnosine and melittin-loaded niosomes in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
Abstract
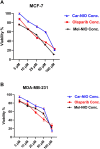
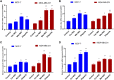
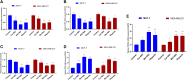
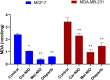
Background: We investigated the anti-cancer effect of carnosine-loaded niosomes (Car-NIO) and melittin-loaded niosomes (Mel-NIO) with olaparib in breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Methods: The thin film method was used for preparing the niosomes and characterized in terms of morphology, size, and polydispersity index (PDI). We further evaluated the impact of these peptides on breast cancer cells viability, RT-qPCR assays, malondialdehyde (MDA) activity, and cell cycle progression, to determine if these are linked to carnosine and melittin's anti-proliferative properties. Results: Car-NIO and Mel-NIO in vitro study inhibited cancer cell viability. They have also upregulated the expression of protein 53 (P53), BCL2-Associated X Protein (Bax), caspase-9, caspase-3, programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), and Forkhead box O3 (FOXO3), while downregulated the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2), poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP 1), and MicroRNA-183 (miRNA-183). The MCF-7 cells were arrested at the G2/M phase in Car-NIO, on the other hand, the MDA-MB-231 cells were arrested at the S phase. While the Mel-NIO and olaparib arrested the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells at the G0/1 phase. Conclusion: Our study successfully declared that Mel-NIO had more anti-cancer effects than Car-NIO in both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Keywords: breast cancer cells; carnosine; cell cycle analysis; melittin; miRNA-183; niosome.
Copyright © 2023 Hussein, Abdelfattah-Hassan, Eldoumani, Essawi, Alsahli, Alharbi, Alzarea, Al-Hejaili and Gaafar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
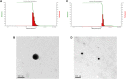
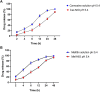
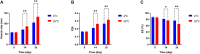
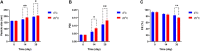
References
-
- Asfour H. Z., Alhakamy N. A., Ahmed O. A., Fahmy U. A., El-Moselhy M. A., Rizg W. Y., et al. (2022). Enhanced healing efficacy of an optimized gabapentin-melittin nanoconjugate gel-loaded formulation in excised wounds of diabetic rats. Drug Deliv. 29, 1892–1902. 10.1080/10717544.2022.2086943 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashmawy A. M., Sheta M. A., Zahran F., Abdel Wahab A. H. (2017). MiRNAs-181a/b as Predictive biomarkers for olaparib sensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer cells. BLJ 13, 221–229. 10.21608/blj.2017.47612 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

