Advances in the application of CRISPR-Cas technology in rapid detection of pathogen nucleic acid
- PMID: 37808520
- PMCID: PMC10552857
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1260883
Advances in the application of CRISPR-Cas technology in rapid detection of pathogen nucleic acid
Abstract
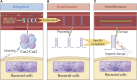
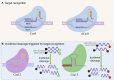
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-associated proteins (Cas) are widely used as gene editing tools in biology, microbiology, and other fields. CRISPR is composed of highly conserved repetitive sequences and spacer sequences in tandem. The spacer sequence has homology with foreign nucleic acids such as viruses and plasmids; Cas effector proteins have endonucleases, and become a hotspot in the field of molecular diagnosis because they recognize and cut specific DNA or RNA sequences. Researchers have developed many diagnostic platforms with high sensitivity, high specificity, and low cost by using Cas proteins (Cas9, Cas12, Cas13, Cas14, etc.) in combination with signal amplification and transformation technologies (fluorescence method, lateral flow technology, etc.), providing a new way for rapid detection of pathogen nucleic acid. This paper introduces the biological mechanism and classification of CRISPR-Cas technology, summarizes the existing rapid detection technology for pathogen nucleic acid based on the trans cleavage activity of Cas, describes its characteristics, functions, and application scenarios, and prospects the future application of this technology.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas; Cas12; Cas13; Cas14; Cas9; pathogen nucleic acid; rapid detection.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Zhong, Li, Qiao, Mao, Fan, Zhong, Imani, Zheng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CRISPR-cas technology: A key approach for SARS-CoV-2 detection.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 12;11:1158672. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1158672. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37214290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas systems for the detection of nucleic acid and non-nucleic acid targets.Nano Res. 2023 Mar 20:1-14. doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-5567-4. Online ahead of print. Nano Res. 2023. PMID: 37359078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Mechanism and Applications of CRISPR/Cas9/Cas12/Cas13/Cas14 Proteins Utilized for Genome Engineering.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;65(3):311-325. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00567-0. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36163606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR technology incorporating amplification strategies: molecular assays for nucleic acids, proteins, and small molecules.Chem Sci. 2021 Mar 2;12(13):4683-4698. doi: 10.1039/d0sc06973f. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34163728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR-Cas-based techniques for pathogen detection: Retrospect, recent advances, and future perspectives.J Adv Res. 2023 Aug;50:69-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.10.011. Epub 2022 Oct 30. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36367481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and Challenges in Cytomegalovirus Detection Methods for Liver Transplant Donors.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 26;13(21):3310. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13213310. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in diagnostic assays for Clostridioides difficile infection in adults.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Dec 10;14:1492511. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1492511. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39720791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology and diagnosis technologies of human metapneumovirus in China: a mini review.Virol J. 2024 Mar 7;21(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02327-9. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38454484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Review of the CRISPR-Cas Technology in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025 Jul 9;2025:9107724. doi: 10.1155/cjid/9107724. eCollection 2025. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40678258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Metapneumovirus: Emergence, Impact, and Public Health Significance.Cureus. 2025 Mar 21;17(3):e80964. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80964. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

