Prevalence and Associated Factors of Adolescent Obesity among Rural School Adolescents in Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 37808524
- PMCID: PMC10558264
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/2957278
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Adolescent Obesity among Rural School Adolescents in Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Overweight and obesity are major risk factors for chronic diseases and are the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Obesity during adolescence is strongly associated with adulthood obesity leading to increased morbidities and mortality. As a developing country undergoing rapid urbanization, Nepal is in a transitional phase where undernutrition coexists with obesity; however, there is a dearth of literature on the status of adolescent obesity in the rural section of Nepal. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of adolescent obesity in a rural district of Nepal and find out its associated factors.
Methods: An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among the adolescent students studying in classes 8, 9, and 10 in four secondary schools of Gosaikunda rural municipality of Rasuwa district, Nepal. Total enumerative sampling was used, and Global School-based Health Survey (GSHS) standard questionnaires were used in collecting the information. Height and weight measurements were taken, and the body mass index was classified according to Asia-Pacific criteria. The collected data were analyzed using "SPSS" version 22. Logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the associated factors, and a p value of ≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
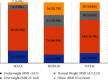
Results: Out of 267 adolescents, 14.6% were obese and 14.6% were overweight. Of the female participants, 39.6% were either obese or overweight, while 12.6% of the male adolescents were overweight/obese. Among the total participants, 16.5% were underweight, including 14.0% females and 20.4% males. Female adolescents were about five times (AOR: 5.2, 95% CI (2.5-10.9), p < 0.01) more likely of being overweight/obese than male adolescents.
Conclusions: More than one-quarter of the adolescents were found to be obese/overweight, and the prevalence was significantly more among female adolescents. It emphasizes the necessity of school-based programs promoting a healthy lifestyle among students to maintain healthy weight status.
Copyright © 2023 Deekshanta Sitaula et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and associated factors of childhood overweight/obesity among primary school children in urban Nepal.BMC Public Health. 2019 Aug 6;19(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7406-9. BMC Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31387571 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with childhood overweight/obesity of private school children in Nepal.Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015 May-Jun;9(3):220-7. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2014.10.219. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2015. PMID: 25434691
-
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Overweight and Obesity among High School Adolescents in Bahir Dar City, Northwest, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Obes. 2021 Mar 9;2021:8846723. doi: 10.1155/2021/8846723. eCollection 2021. J Obes. 2021. PMID: 33777450 Free PMC article.
-
Overweight and its associated risk factors among urban school adolescents in Nepal: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2016 May 20;6(5):e010335. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010335. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27207624 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity among School Children and Adolescents in Indian Population.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Mar-Apr;28(2):104-116. doi: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_365_23. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38911116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and factors associated with overweight and obesity among adolescents in Nagarjun municipality: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Public Health. 2024 Oct 31;2(2):e001675. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-001675. eCollection 2024 Dec. BMJ Public Health. 2024. PMID: 40018609 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of a Nurse-Led Physical Activity Program on Reducing Obesity and Enhancing Quality of Life Among Obese Adolescents: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 May;17(Suppl 1):S673-S675. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1625_24. Epub 2025 Feb 10. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40511071 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Who. Obesity. 2022. https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity .
-
- Abarca-Gómez L., Abdeen Z. A., Hamid Z. A., et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: a pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. The Lancet . 2017;390(10113):2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32129-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials