Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Rhabdomyolysis: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 37808625
- PMCID: PMC10558265
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6396576
Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Rhabdomyolysis: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
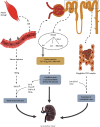
Background: Rhabdomyolysis (RM) refers to a clinical syndrome in which muscle cells are damaged by various causes and the clinical manifestations are mainly muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a serious complication of RM with complex mechanisms and high mortality. Therefore, understanding the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations, early diagnosis and treatment of RM are crucial to improve its prognosis.
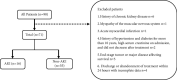
Method: Analysis of medical records of RM patients admitted to Tianjin Medical University General Hospital from October 2019 to October 2022. Statistical software SPSS 25.0 was used to analyze the data. The risk factors of RM-complicated AKI were analyzed by logistic regression. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted, the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated, and the optimal cutoff value was determined by the Youden index. P < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference between the groups.
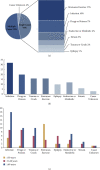
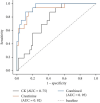
Result: Among the 71 patients, the median age of the patients was 53.0 (30.0, 71.0) years and was 2.5 times higher in men than in women. Infection was the most common etiology. History of alcohol consumption, CK, and creatinine were independent influencing factors for AKI due to RM. Logistic regression analysis showed that CK combined with creatinine had a better predictive value than the single index.
Conclusion: Our study revealed the clinical and laboratory characteristics of RM in the population attending the Tianjin Medical University General Hospital in the last three years, which is a reference for future multicenter, prospective studies.
Copyright © 2023 Keke Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severe burns complicated by early acute kidney injury.Burns. 2020 Aug;46(5):1100-1106. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2019.11.018. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Burns. 2020. PMID: 31839503
-
Risk factors for severe acute kidney injury among patients with rhabdomyolysis.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Nov 23;21(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02104-0. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33225908 Free PMC article.
-
Rhabdomyolysis: a 10-year retrospective study of patients treated in a medical department.Eur J Emerg Med. 2019 Jun;26(3):199-204. doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000510. Eur J Emerg Med. 2019. PMID: 29068810
-
Rhabdomyolysis: A syndrome to be considered.Med Clin (Barc). 2022 Mar 25;158(6):277-283. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2021.09.025. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Med Clin (Barc). 2022. PMID: 34872769 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Non-traumatic rhabdomyolysis: Background, laboratory features, and acute clinical management.Clin Biochem. 2017 Aug;50(12):656-662. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.02.016. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Clin Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28235546 Review.
Cited by
-
Rhabdomyolysis in intensive care unit-distinctive clinical indicators and prognosis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Feb 19;25(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-02964-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39972271 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin subunit beta 6 is a potential diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury in patients with diabetic kidney disease: a single cell sequencing data analysis.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2409348. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2409348. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39356055 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Analysis of Risk Factors Associated with Rhabdomyolysis in Snakebite Victims.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Nov 26;17:5535-5546. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S479291. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39619128 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction in acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2393262. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2393262. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39192578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uric acid in predicting the traumatic rhabdomyolysis induced acute kidney injury; a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 5;25(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03509-x. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38443920 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
