This is a preprint.
A Window into Mammalian Basement Membrane Development: Insights from the mTurq2-Col4a1 Mouse Model
- PMID: 37808687
- PMCID: PMC10557719
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.27.559396
A Window into Mammalian Basement Membrane Development: Insights from the mTurq2-Col4a1 Mouse Model
Update in
-
An mTurq2-Col4a1 mouse model allows for live visualization of mammalian basement membrane development.J Cell Biol. 2024 Feb 5;223(2):e202309074. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202309074. Epub 2023 Dec 5. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38051393 Free PMC article.
Abstract
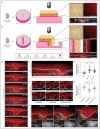
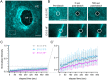
Basement membranes (BMs) are specialized sheets of extracellular matrix that underlie epithelial and endothelial tissues. BMs regulate traffic of cells and molecules between compartments, and participate in signaling, cell migration and organogenesis. The dynamics of mammalian BMs, however, are poorly understood, largely due to a lack of models in which core BM components are endogenously labelled. Here, we describe the mTurquoise2-Col4a1 mouse, in which we fluorescently tag collagen IV, the main component of BMs. Using an innovative Planar-Sagittal live imaging technique to visualize the BM of developing skin, we directly observe BM deformation during hair follicle budding and basal progenitor cell divisions. The BM's inherent pliability enables dividing cells to remain attached to and deform the BM, rather than lose adhesion as generally thought. Using FRAP, we show BM collagen IV is extremely stable, even during periods of rapid epidermal growth. These findings demonstrate the utility of the mTurq2-Col4a1 mouse to shed new light on mammalian BM developmental dynamics.
Figures
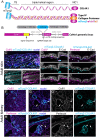
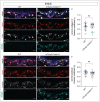
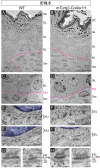
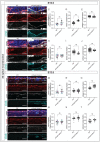
References
-
- ALBINI A. & NOONAN D. M. 2010. The ‘chemoinvasion’ assay, 25 years and still going strong: the use of reconstituted basement membranes to study cell invasion and angiogenesis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 22, 677–689. - PubMed
-
- BANERJEE S., LO W.-C., MAJUMDER P., ROY D., GHORAI M., SHAIKH N. K., KANT N., SHEKHAWAT M. S., GADEKAR V. S. & GHOSH S. 2022. Multiple roles for basement membrane proteins in cancer progression and EMT. European Journal of Cell Biology, 101, 151220. - PubMed
-
- BEHRENS D. T., VILLONE D., KOCH M., BRUNNER G., SOROKIN L., ROBENEK H., BRUCKNER-TUDERMAN L., BRUCKNER P. & HANSEN U. 2012. The epidermal basement membrane is a composite of separate laminin- or collagen IV-containing networks connected by aggregated perlecan, but not by nidogens. J Biol Chem, 287, 18700–9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
