This is a preprint.
Genome-wide CRISPR activation screen identifies JADE3 as an antiviral activator of NF-kB
- PMID: 37808733
- PMCID: PMC10557722
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.09.29.560128
Genome-wide CRISPR activation screen identifies JADE3 as an antiviral activator of NF-kB
Update in
-
Genome-wide CRISPR activation screen identifies JADE3 as an antiviral activator of NF-kB-dependent IFITM3 expression.J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):107153. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107153. Epub 2024 Mar 9. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38462163 Free PMC article.
Abstract
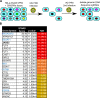
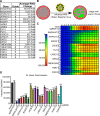
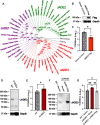
The innate immune system features a web of interacting pathways that require exquisite regulation. To identify novel nodes in this immune landscape we conducted a gain of function, genome-wide CRISPR activation screen with influenza A virus. We identified both appreciated and novel antiviral genes, including JADE3 a protein involved in directing the histone acetyltransferase HBO1 complex to modify chromatin and regulate transcription. JADE3 is both necessary and sufficient to restrict influenza A virus infection. Interestingly, expression of the closely related paralogues JADE1 and JADE2 are unable to restrict influenza A virus infection, suggesting a distinct function of JADE3. We identify both shared and unique transcriptional signatures between uninfected cells expressing JADE3 and JADE2. These data provide a framework for understanding the overlapping and distinct functions of the JADE family of paralogues. Specifically, we find that JADE3 expression activates the NF-kB signaling pathway, consistent with an antiviral function. Therefore, we propose JADE3, but not JADE1 or JADE2, activates an antiviral genetic program involving the NF-kB pathway to restrict influenza A virus infection.
Figures



References
-
- Medzhitov R., Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature, 2008. 454(7203): p. 428–435. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
