Unrelenting Vision Loss: The Virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 37809162
- PMCID: PMC10558182
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44786
Unrelenting Vision Loss: The Virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
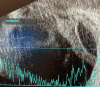
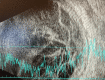
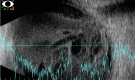
A 37-year-old Hispanic male with a recent history of COVID-19 infection and type 2 diabetes mellitus was admitted to the hospital with shortness of breath, chest pain, and hyperglycemia. Eye exam and imaging findings indicated endogenous endophthalmitis confirmed by blood cultures that speciated to Klebsiella pneuomoniae. The patient's eye condition progressed, ultimately resulting in no light perception less than a month after the initial evaluation. Due to the rapidly progressive nature of Klebsiella endogenous endophthalmitis, we recommend that primary teams consult ophthalmology for close monitoring of patients with a high index of suspicion.
Keywords: endophthalmitis; intravitreal antibiotic; klebsiella endophthalmitis; klebsiella pneumoniae; subretinal abscess.
Copyright © 2023, Prasad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia: 3 cases report and literature review (Article in Chinese) Wang F, Tao Y, Sun B, Tong ZH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31189230/ Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2019;42:438–443. - PubMed
-
- Prognostic factors and outcomes in endogenous Klebsiella pneumoniae endophthalmitis. Ang M, Jap A, Chee SP. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011;151:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Risk factors for endogenous endophthalmitis secondary to klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess: 20-year experience in Southern Taiwan. Sheu SJ, Kung YH, Wu TT, Chang FP, Horng YH. Retina. 2011;31:2026–2031. - PubMed
-
- Endogenous Klebsiella endophthalmitis. Ang LP, Lee HM, Au Eong KG, Yap EY, Lim AT. Eye (Lond) 2000;14:855–860. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
