Can we recognize severe community-acquired pneumonia without pneumonia severity index? Use of modified qSOFA with procalcitonin
- PMID: 37809503
- PMCID: PMC10559344
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19937
Can we recognize severe community-acquired pneumonia without pneumonia severity index? Use of modified qSOFA with procalcitonin
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to analyze the diagnostic value of Quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (qSOFA), modified qSOFA, National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and NEWS + Lactate (NEWS + L) scores in the detection of severe community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
Methods: This research is a retrospective cohort study. Patients admitted to the Emergency Department (ED) with the diagnosis of CAP were divided into severe and mild pneumonia regarding their Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) scores. The accuracies of lactate, procalcitonin (PCT) values, NEWS and qSOFA scores, as well as score combinations (NEWS + L and qSOFA + PCT) in predicting patients with severe CAP were analyzed.
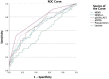
Results: Median qSOFA value in the severe CAP group (0 [IQR 0-1]) was found to be higher than median qSOFA value (0 [IQR 0-0]) in the mild CAP group (p < 0.001). The rate of qSOFA positivity (qSOFA ≥ 2) was significantly higher in the severe CAP group (17.1%, n = 21) compared to the mild CAP group (1.3%, n = 1) (p < 0.001). Median qSOFA + PCT for the severe CAP group (2 [IQR 1-2]) was higher than the mild CAP group (1 [IQR 0-1]) (p < 0.001). Mean NEWS score for severe CAP (4.95 ± 3.09) was found to be 1.69 (95% CI 0.92-2.46) higher than mean NEWS score of the mild CAP group (3.26 ± 2.39) (p < 0.001). The severe CAP NEWS + L score (6.97 ± 3.71) was higher than the mild CAP NEWS + L score (4.94 ± 2.48) (p < 0.001). Blood lactate level was not significant in the evaluation of severe CAP (p = 0.221). PCT (AUROC = 0.685 [95% CI 0.610-0.760]; p = 0.038), NEWS score (AUROC = 0.658 95% CI [0.582-0.733]; p < 0.001), qSOFA (AUROC = 0.686) were calculated to have adequate accuracy for the detection of severe CAP. [95% CI 0.613-0.759]; p = 0.037), NEWS + L score (AUROC = 0.665 [95% CI 0.589-0.740]; p = 0.038). The qSOFA + PCT score (AUROC = 0.758 [95% 0.691-0.825]; p = 0.034) was also found to be a highly accurate predictor of severe CAP.
Conclusion: In this study, we found a combination of qSOFA and PCT to be the most reliable method of detecting severe CAP.
Keywords: Community-acquired pneumonia; Lactate; Procalcitonin; Scoring systems.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Ustaalioğlu İ., Ak R., Öztürk T.C., Koçak M., Onur Ö. Investigation of the usability of the REMS, RAPS, and MPM II0 scoring systems in the prediction of short-term and longterm mortality in patients presenting to the emergency department triage. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2022 Jun 16 doi: 10.1007/s11845-022-03063-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous